Chapter 2 Final Accounts (Financial Statements) of Partnership Firm
Chapter 2 Final Accounts (Financial Statements) of Partnership Firm
Accoutancy
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
1. Select the correct answer for each questions :
1. In which year partnership Act was implemented in India ?
(A) 1923
(B) 1932
(C) 1947
(D) 1956
2. In which proportion profit-loss will be shared between the partners made in the partnership deed ?
(A) Capital proportion
(B) Gaining ratio
(C) Sacrificing ratio
(D) if no provision is Equal proportion
3. Credit balance of trading account represents …………………
(A) gross profit
(B) net profit
(C) gross loss
(D) net loss
4. Goods returned debit means ……………………
(A) purchase
(B) purchase return
(C) sales
(D) sales return
5.Goods returned credit means …………………
(A) purchase return
(B) sales return
(C) purchase
(D) sales
6. Which balance is represented by bank overdraft ?
(A) Debit balance
(B) Credit balance
(C) Debit and Credit
(D) None of the above
7. Where will you disclose the credit balance of profit and loss account which is shown in the trial balance ?
(A) Trading A/c
(B) Profit and loss A/c
(C) Profit and loss appropriation A/c
(D) Capital/current A/c
8. Which transaction is shown at the debit side of the profit and loss appropriation account ?
(A) Interest on drawings
(B) Interest on debit balance of current A/c
(C) Net profit
(D) Amount to be transferred to general reserve
9. Generally, which balance is maintained by current account ?
(A) debit
(B) credit
(C) debit or credit
(D) None of the above
10. The financial position of business is disclosed by ………………
(A) Trial balance
(B) Trading A/c
(C) Balance sheet
(D) Profit and loss A/c
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
2. Describe the objectives of the preparation of final accounts of a partnership firm.
Answer:
The objectives of preparing final accounts for a partnership firm are:
1. Determining Gross Profit or Loss: By creating a trading account, the firm can assess its gross profit or loss, aiding in evaluating operational performance.
2. Calculating Net Profit or Loss: The profit and loss account helps in determining the net profit or loss, providing insights into the overall profitability of the firm.
3. Identifying Divisible Profit or Loss: Through the profit and loss appropriation account, the firm can identify distributable profits after accounting for personal transactions and partner provisions.
4. Assessing Financial Status: Preparation of the balance sheet reveals the financial position of the firm by presenting information on assets, liabilities, receivables, payables, and capital.
5. Meeting Taxation Requirements: Final accounts are crucial for tax purposes as they aid in determining the taxable income of the firm, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
3. Explain in brief, the method of the preparation of final accounts of a partnership firm.
Answer :-
In a partnership firm, all economic transactions are initially recorded in the journal, a subsidiary book. Then, these transactions are posted to the ledger, and the balances of each account are determined. These balances are subsequently compiled in the trial balance as of a specific date.
Based on this trial balance and any provided adjustments or additional information, the financial results and financial position of the business are determined through the preparation of the following necessary accounts and statements:
1. Trading Account: This account records transactions related to the purchase and sale of goods, returns, purchase expenses, and closing stock to ascertain gross profit or loss. The result (gross profit or loss) from the Trading Account is transferred to the Profit and Loss Account.
2. Profit and Loss Account: Transactions of revenue expenses and incomes are recorded here to determine the net profit or loss. Expenses such as administrative, selling-distribution, financial expenses, and revenues are recorded on the debit and credit sides, respectively. The net profit or loss is then transferred to the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
3. Profit and Loss Appropriation Account: This special account illustrates the distribution of profit and loss among partners. Partner-related transactions such as interest on capital, salary, bonus, commission, etc., are recorded on the debit side, while interest on drawings, etc., are recorded on the credit side. The net divisible profit or loss is transferred to partners’ capital or current accounts.
4. Partners’ Capital Accounts: These accounts track partners’ transactions with the firm.
– Under the fluctuating capital account method, all partner-related transactions are recorded here, and the final balance is transferred to the balance sheet.
– Under the fixed capital account method, permanent capital changes are recorded in the capital account, while other transactions are recorded in the partners’ current accounts. The final balance of these accounts is also transferred to the balance sheet.
5. Balance Sheet: This statement reflects the financial position of the business at the end of the year.
– On the capital liability side, partner capital account balances, current account balances, reserves, and current and non-current liabilities are shown.
– On the asset-receivable side, fixed assets, intangible assets, investments, current assets, deferred revenue expenditure, etc., are shown. The total of both sides must be equal.
By meticulously preparing these accounts and statements, the financial performance and position of the partnership firm can be accurately assessed and presented.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
4. State list of tangible and intangible assets.
Answer :-
Tangible assets comprise physical assets that have a tangible presence, including land, buildings, leasehold properties, vehicles, machinery, furniture and fittings, and loose tools.
On the other hand, intangible assets lack a physical presence but hold significant value, such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and goodwill.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
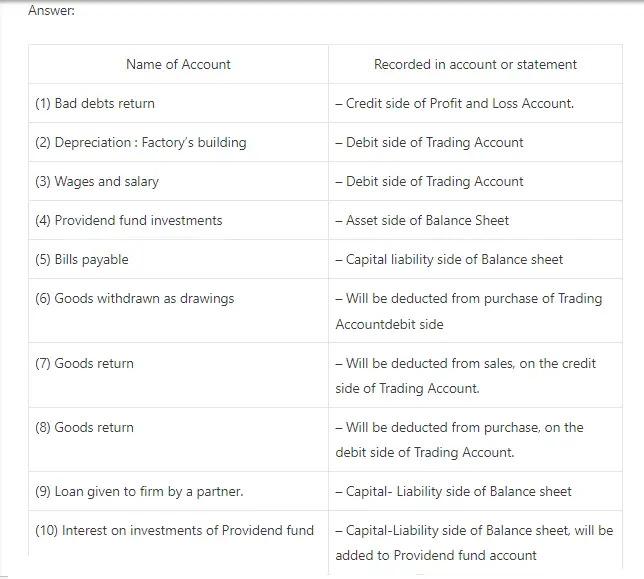
5. Where will you disclose the following items given in a trial balance during the preparation of a final account of a partnership firm :
(1) Bad debts returned (2) Depreciation : factory’s building (3) Wages and salary (4) Providend fund investments (5) Bills payable (6) Goods withdrawn as drawings (7) Goods return credit (8) Goods return debit (9) Loan given to firm by a partner (10) Interest on investments of providend fund.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
6. Where will you disclose the effects of the following adjustments during the preparation of final accounts of a partnership firm :
(1) Closing stock of stationery (2) Unrecorded credit sales (3) Commission payable to partner on net profit (4) Goods withdrawn by partner for personal use. (5) Interest on debit balance of Partners’ current account (6) Certain amount is written off from leasehold property (7) Receivable income (outstanding income) (8) Prepaid expenses (9) Discount reserve on debtors.
| Adjustments | Treatment |
|---|---|
| (1) Closing stock of stationery | (i) Will be deducted from stationery expense, on the debit side of Profit and Loss A/c. (ii) On asset side of Balance sheet, as closing stock of stationery. |
| (2) Unrecorded Credit sales | (i) Will be added to sales A/c, on the credit side of Trading A/c (ii) Will be added to debtors, on asset side, in Balance-sheet. |
| (3) Commission payable to partner on net profit. | (i) Debit side of profit and loss Appropriation A/c (ii) Credit side of Partner’s capital/current A/c |
| (4) Goods withdrawn by partner for personal use | (i) Will be deducted from purchase A/c, on debit side of Trading A/c. (ii) Debit side of partners’ capital/current A/c. |
| (5) Interest on debit balance of partner’s current account | (i) Debit side of partners current A/c (ii) Credit side of profit-loss Appropriation A/c. |
| (6) Certain amount is written off from leasehold property. | (i) Debit side of Profit and Loss A/c. leasehold asset written off. (ii) Deducted from leasehold asset on asset side of balance sheet. |
| (7) Receivable income (Outstanding income) | (i) Will be added to respective income, on credit side of Profit and Loss A/c. (ii) Balance sheet -Asset side. |
| (8) Prepaid expense | (i) Will be deducted from respective expense, on debit side of Trading A/c or on debit side of Profit and Loss A/c. (ii) Balance sheet -Asset side. |
| (9) Discount reserve on debtors | (i) Debit side of Profit and Loss A/c (ii) Will be deducted from debtors, on asset side of Balance sheet. |
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
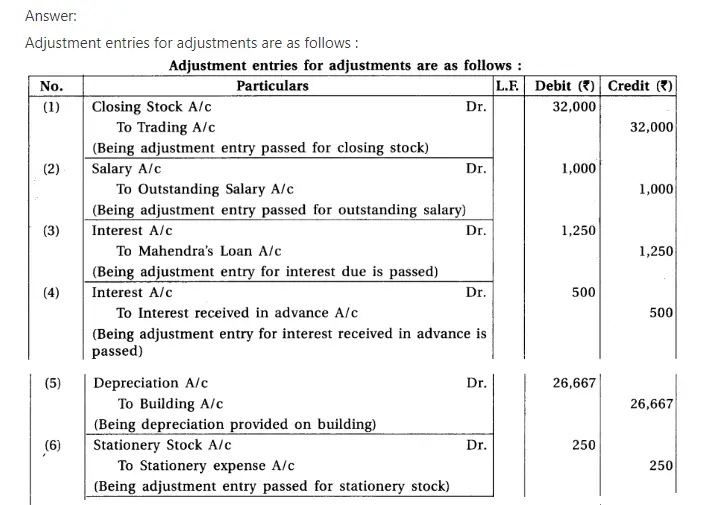
7. Write adjustment entries for the following adjustments :
(1) Book value of stock is ₹ 40,000, but its market value is 20% less than the book value. (2) Salary outstanding ₹ 1,000. (3) Mahendra landed loan of ₹ 25,000 to the firm, but 10% for 6 months is outstanding on it. (4) Interest received in advance ₹ 500. (5) Provide depreciation at 8% for 8 months on a building of ₹ 5,00,000. (6) Closing stock of stationery at the end of the accounting period is ₹ 250. (7) Closing balance at the end of accounting period, of debtors of business is ₹ 50,000, out which written off ₹ 4,500 as bad debts. Provide 10% bad debts reserve on debtors. (8) One partner has withdrawn goods of ₹ 5,000 for personal use, this transaction is not recorded. (9) Goods of ₹ 3,000 destroyed by fire. Insurance company has admitted the claim of 80%.

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
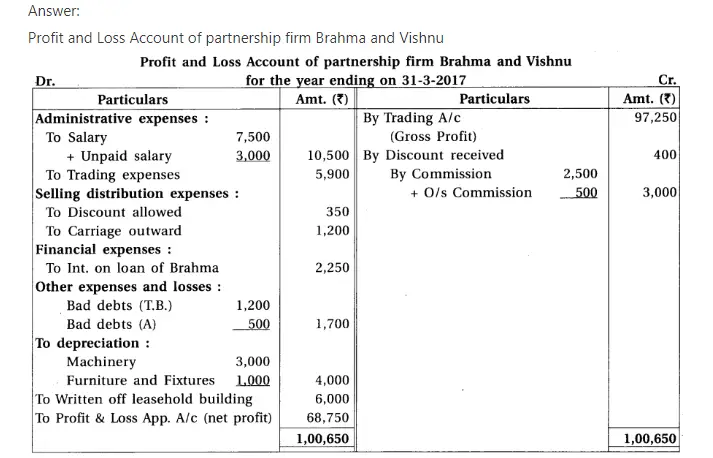
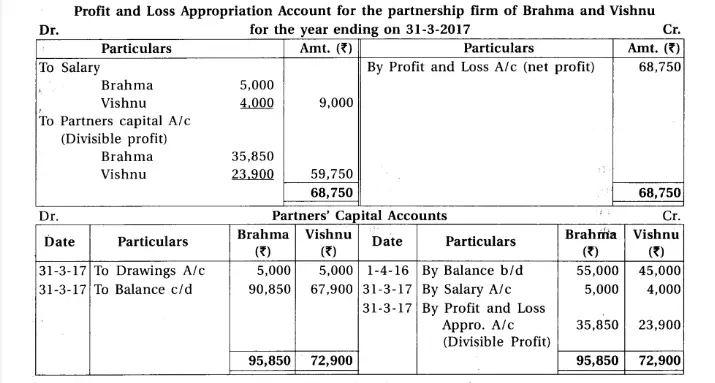
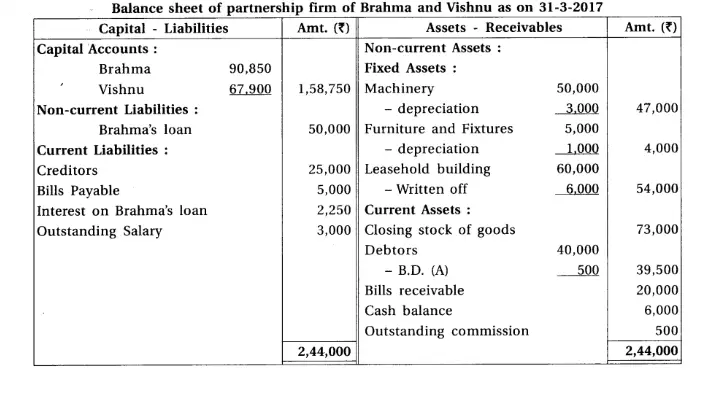
8. Brahma and Vishnu are partners of a firm sharing profit-loss in the proportion 3 : 2. From the trial balance dated 31-3-2017 and adjustments, prepare annual accounts of the firm :
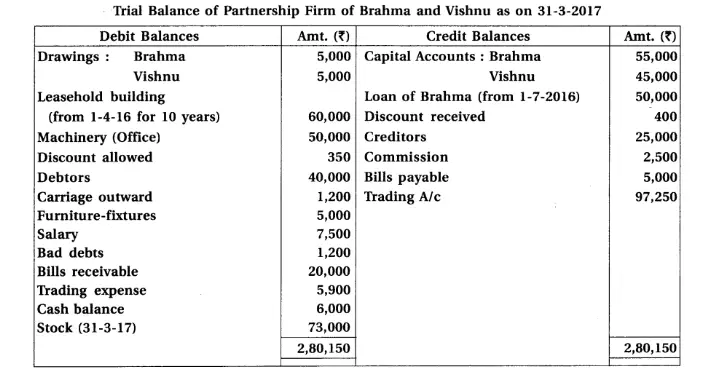
Adjustments : (1) Provide depreciation 6% on machinery and 20% on furniture fixtures. (2) Written off ₹ 500 from debtors as bad debts. (3) Annual salary of ₹ 5,000 and ₹ 4,000 payable to Brahma and Vishnu respectively. (4) Commission ₹ 500 is receivable. (5) Outstanding salary ₹ 3,000.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
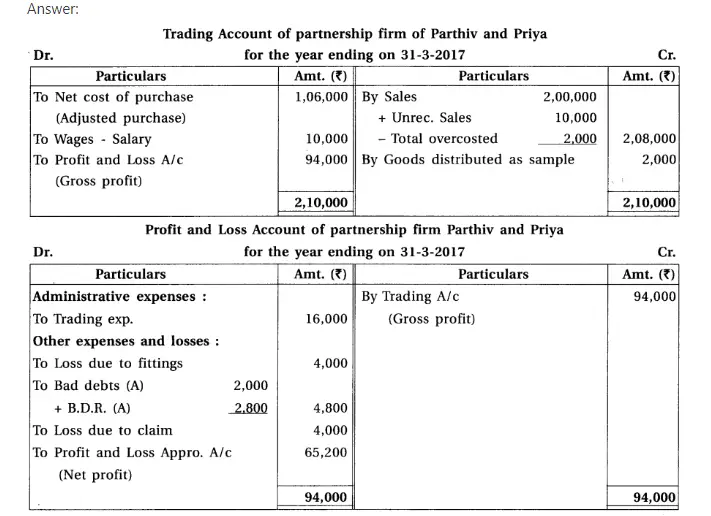
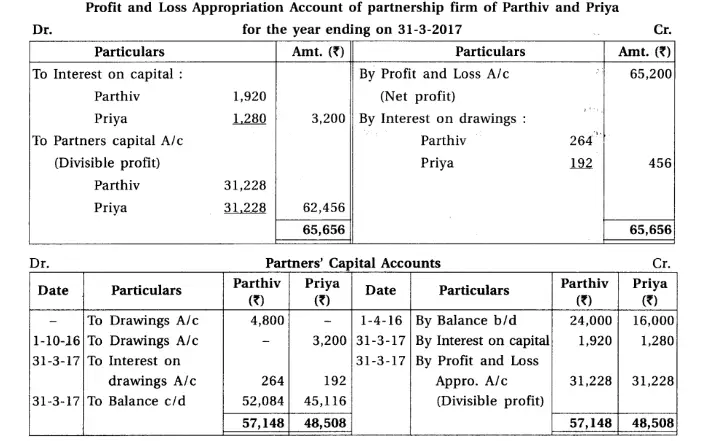
9.Parthiv and Priya are the partners of a partnership firm. From the Trial balance dated 31-3-2017 and adjustments, prepare final accounts of a partnership firm.

Note : Net cost of purchase means adjusted purchase.
Adjustments : (1) Provide interest 8% on capital and 12% on drawings. Parthiv had withdrawn ₹ 400 at the end of each month and Priya had withdrawn on 1-10-16. (2) Credit sales of ₹ 10,000 is not recorded and total of sales book of March is overcast by ₹ 2,000. (3) Write off additional bad debts of ₹ 2,000 and provide 5% bad debts reserve on debtors. (4) Furniture of ₹ 4,000 became obsolete, which is not recorded in the books. (5) A court has finalised claim of ₹ 4,000; for not meeting agreement to provide goods to a customer. (6) Outstanding wages of ₹ 2,000 is recorded to wages account but outstanding wages account is not recorded in the trial balance.
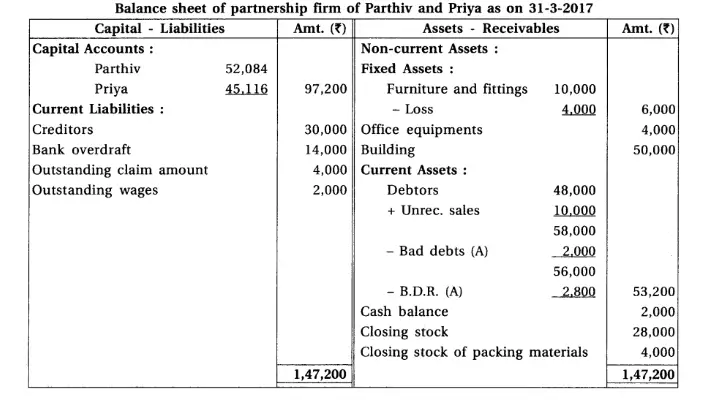
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
10. Luv and Kush are partners of a partnership firm. They distribute 60% profit in the ratio of 3 : 2 and remaining in the proportipn of 2 : 1. From the trial balance of the firm dated 31-3-17 and adjustments prepare profit a nd loss appropriation account, current accounts of partners and balance sheet of the firm.
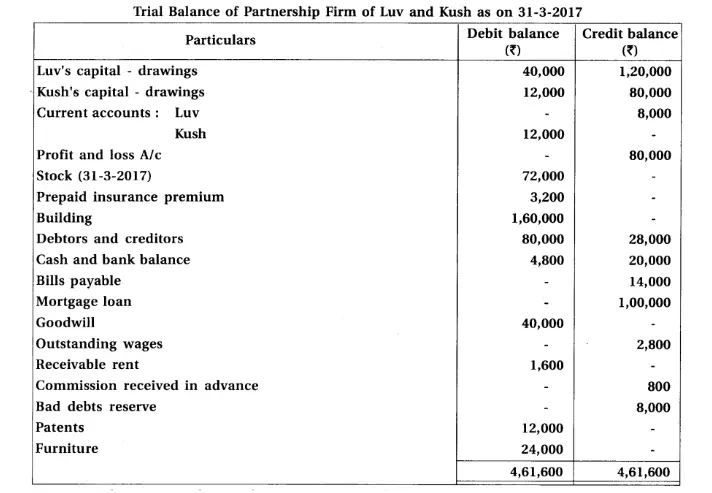
Adjustments : (1) Provide interest on capital at 6% and on drawings at 10 %. (2) Provide 10% interest on opening balance of current accounts. (3) Monthly salary of ₹ 1,800 is outstanding, payable to Kush. (4) After information of above mentioned adjustments, on remaining profit 10% commission is payable to Kush.

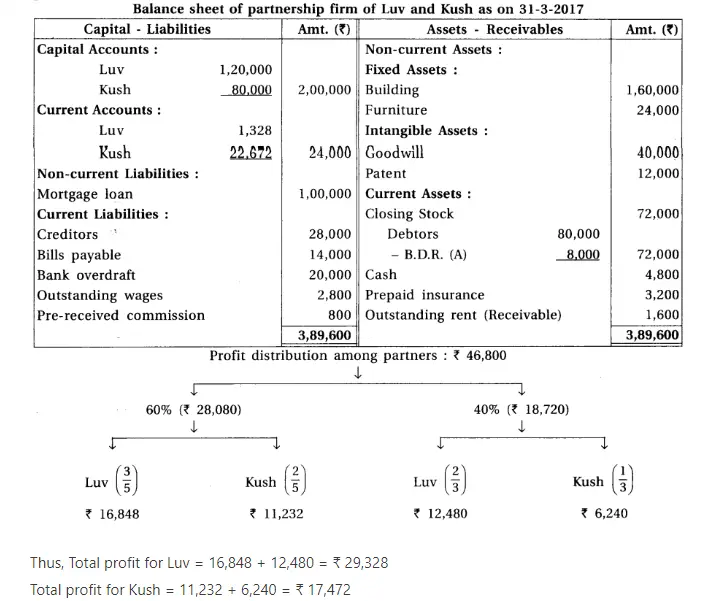
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
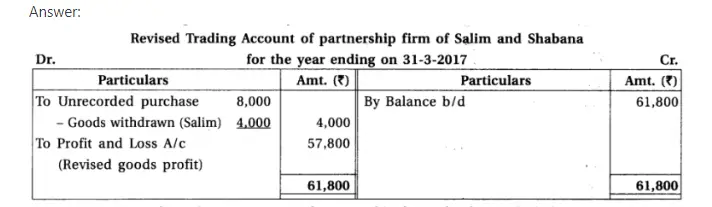
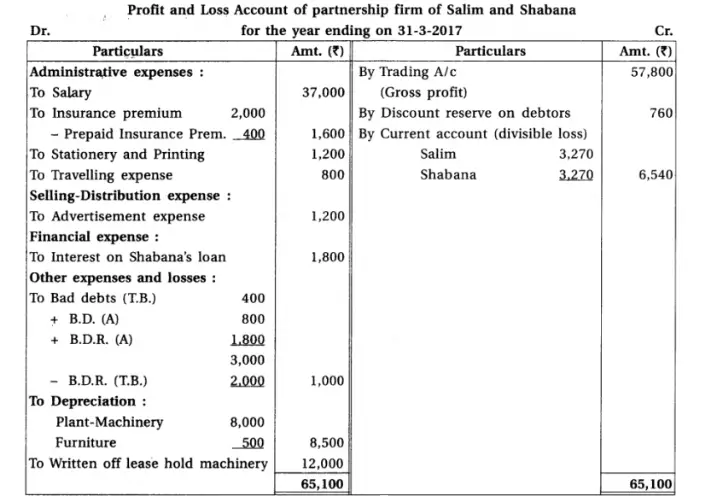
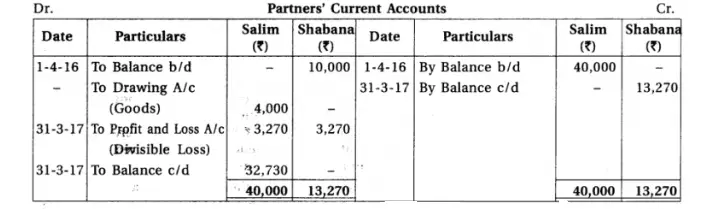
11.From the Trial Balance and adjustments of partnership firm of Salim and Shabana, prepare final accounts of partnership firm. Trial Balance of partnership firm of Salim and Shabana as on 31-3-2017
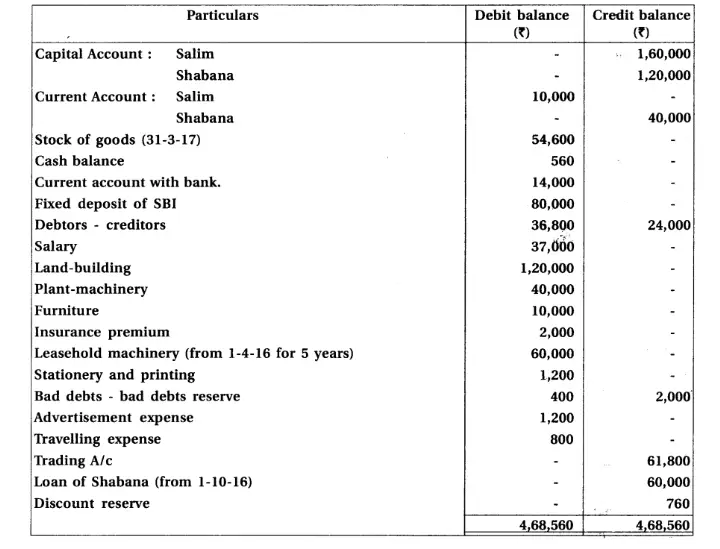
Adjustments : (1) Salim withdrew goods of ₹ 4,000 for personal use. It is not recorded in the books. (2) Goods of ₹ 8,000 purchased at the end of the accounting year, which is not recorded. (3) Prepaid insurance is ₹ 400. (4) From debtors ₹ 800 is not recoverable. Provide 5% bad debts reserve on debtors. (5) Discount reserve on debtors is not required. (6) Provide depreciation on plant-machinery at 20% and on furniture at 5%.
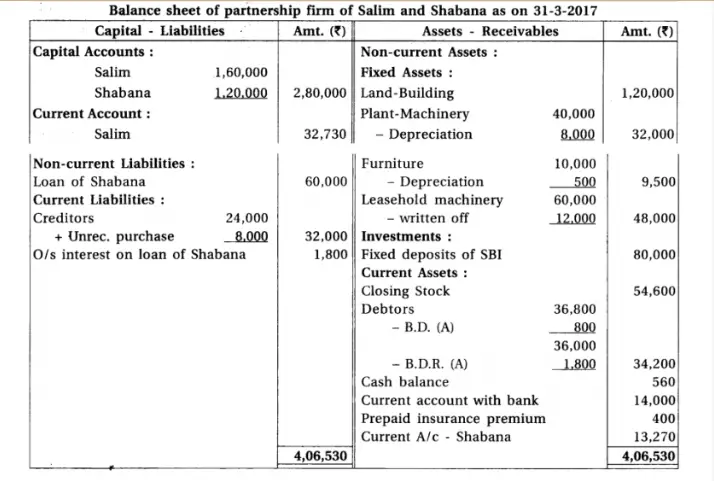

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
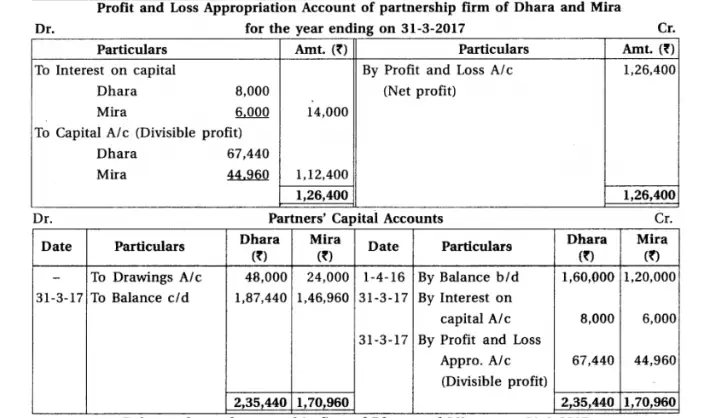
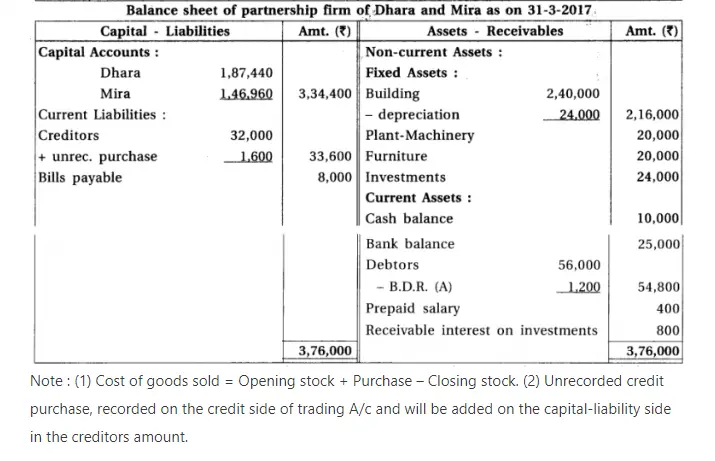
12. Dhara and Mira are partners sharing profit-loss in the proportion of 3 : 2. Final accounts of their partnership firm are as follows :
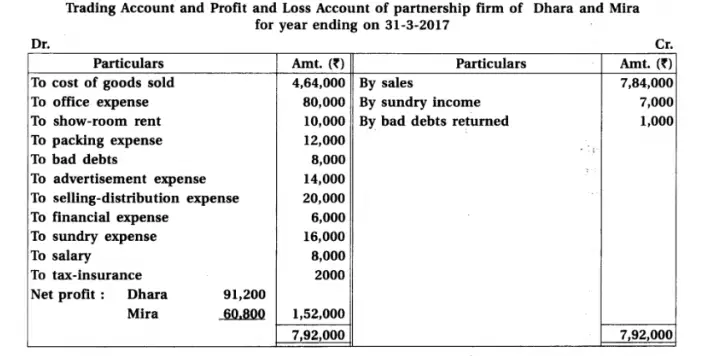
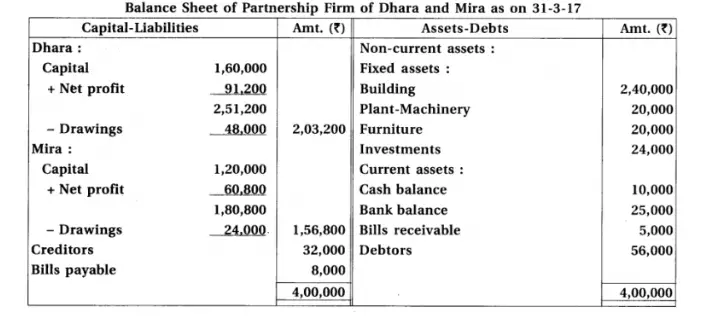
After preparation of annual accounts, it is found that :
(1) 5% interest on capital is not calculated. (2) 10% depreciation on building is to be provided. (3) Prepaid salary is of ₹ 400. (4) Interest on investments not received ₹ 800. (5) Bad debts reserve of ₹ 1,200 is to be maintained. (6) Credit purchase of ₹ 1,600 is not recorded.
Prepare revised Trading account/Profit and loss a/c, Profit and loss appropriation a/c and Balance sheet.


Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
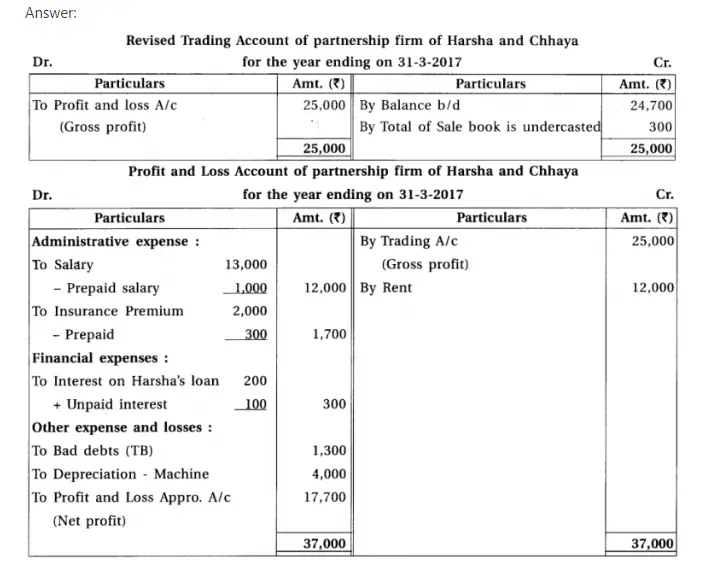
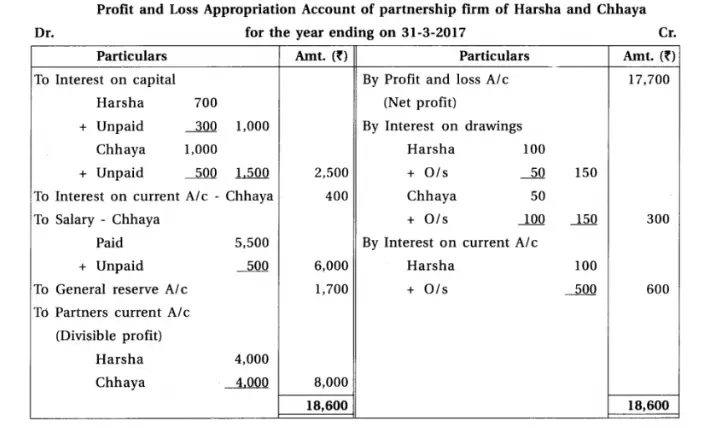
13. Harsha and chhaya are partners of a partnership firm. From the following information prepare final accounts :
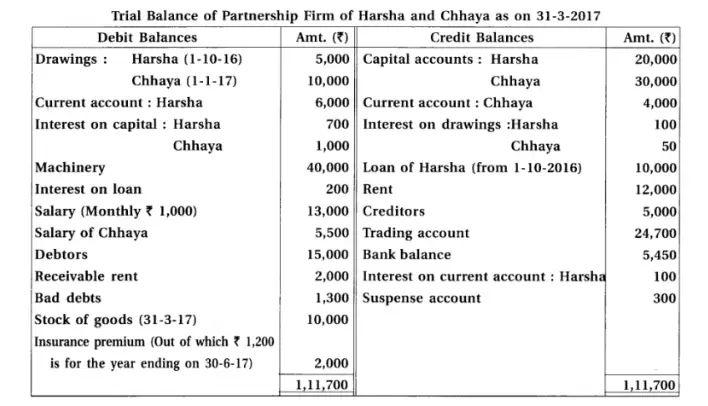
Adjustments : (1) Provide interest 5% on capital, 6% on drawings and 10% on opening balance of current a/c. (2) Provide 10% depreciation on machines. (3) Monthly salary of Chhaya is ₹ 500. (4) Total of sales book is under cast by ₹ 300. (5) ₹ 1,700 are to be transferred to general reserve.
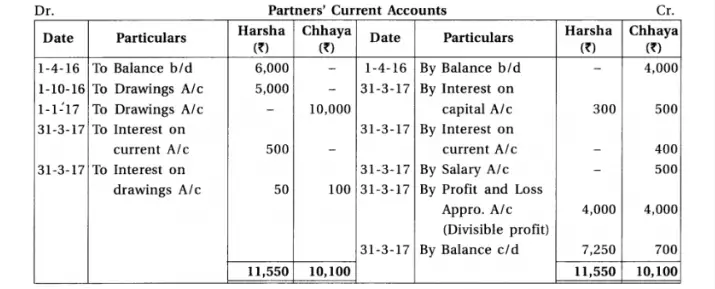
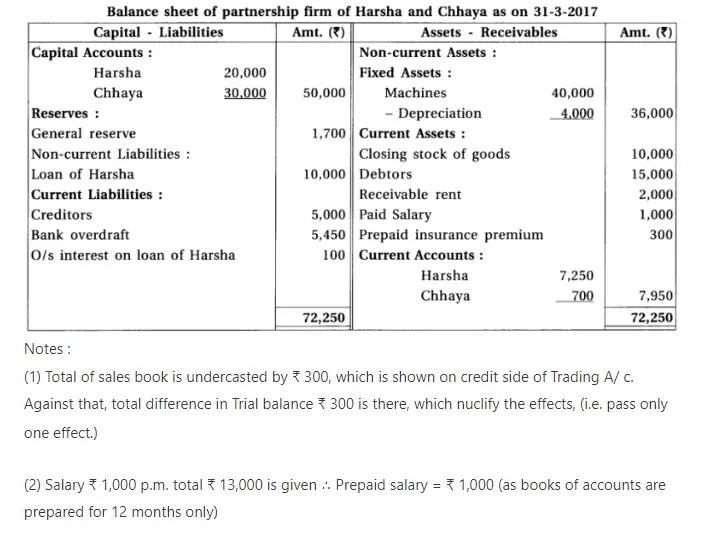

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
14. Dharma and Karma are partners sharing profit-loss in their capital ratio. From the following information prepare their final accounts.
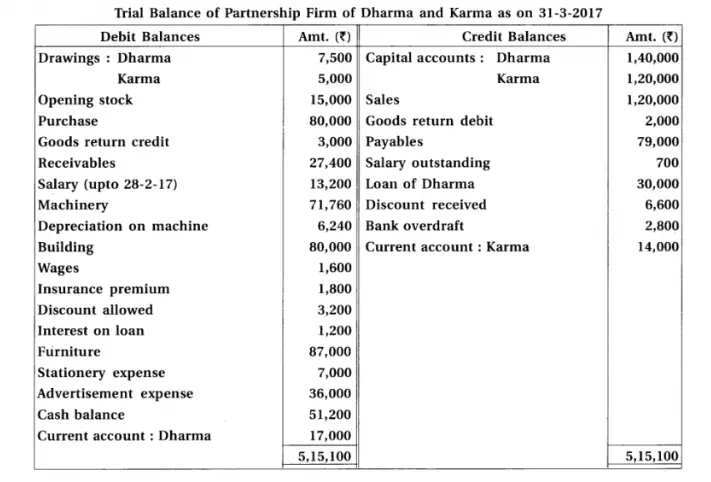

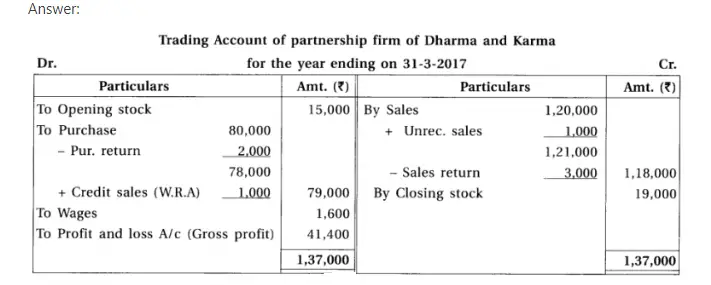
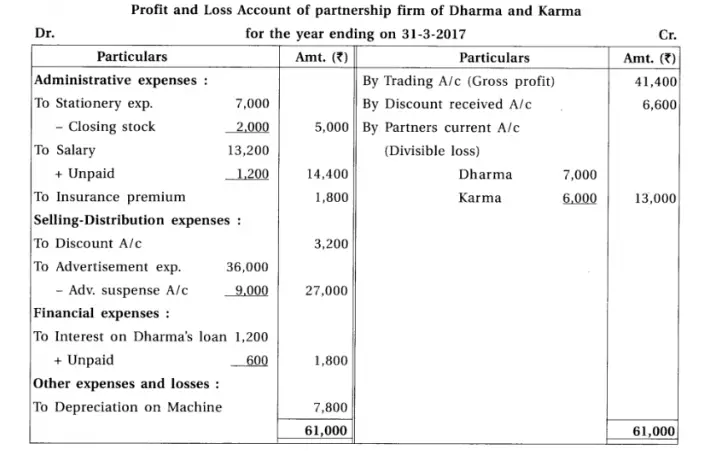
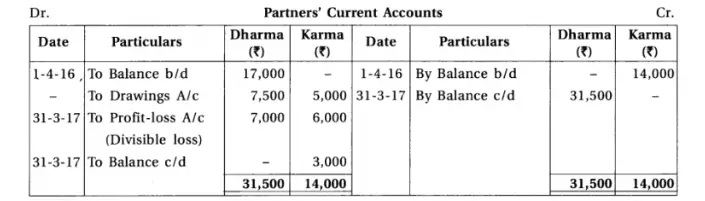
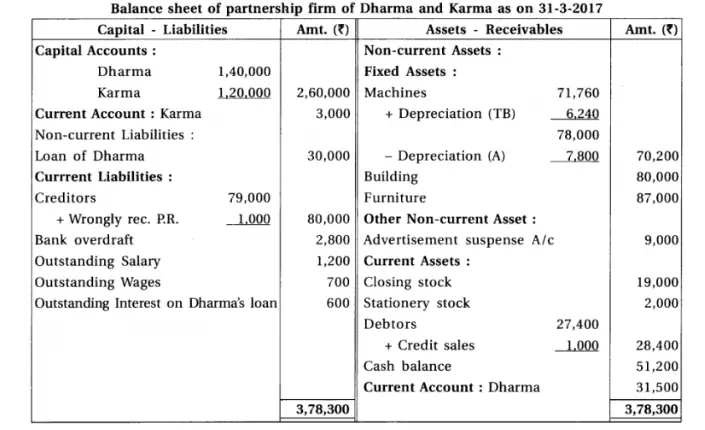

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
15. With consideration of following trial balance and adjustments of Harsh and Yesha, prepare final accounts for the year ending on 31-3-17 of their firm.
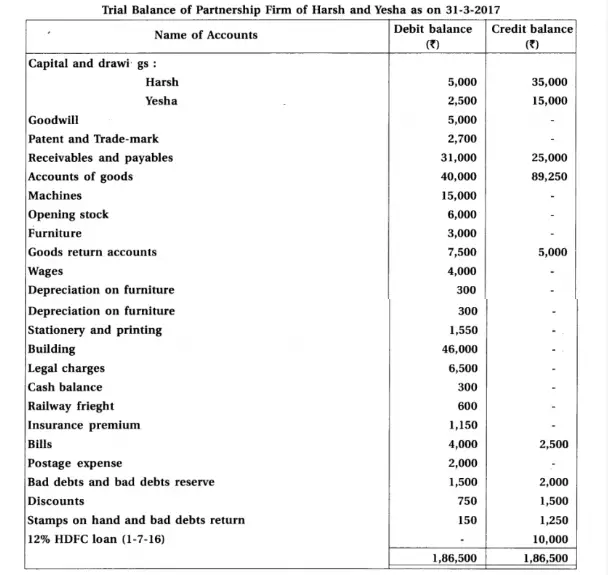

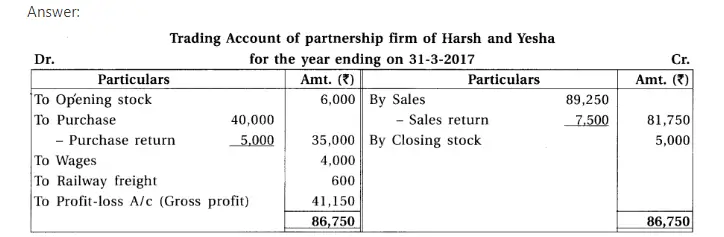
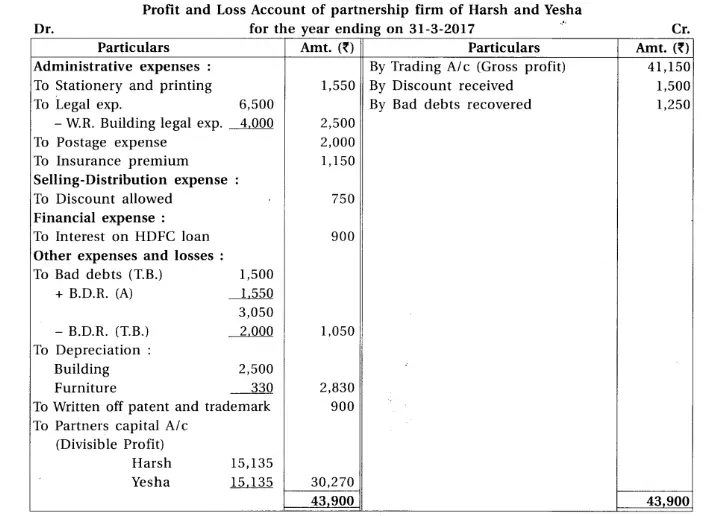
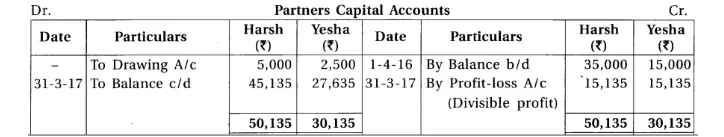
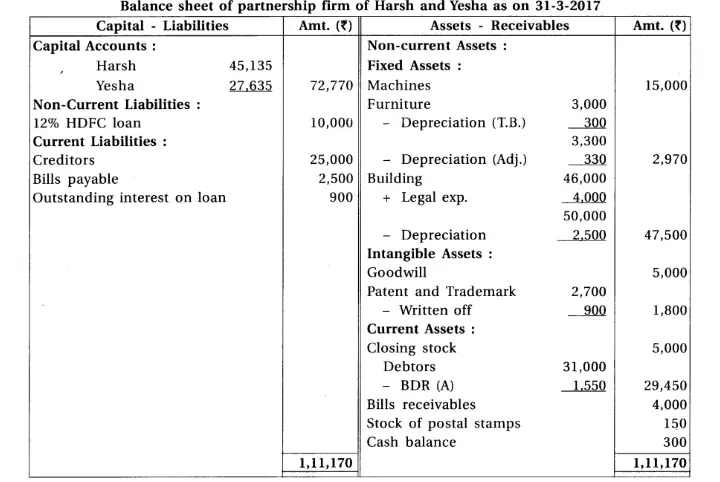
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
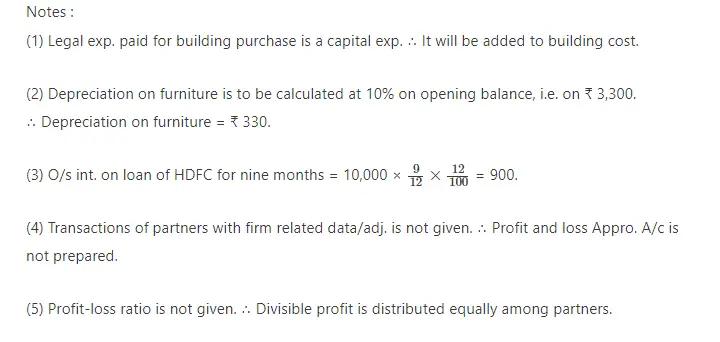
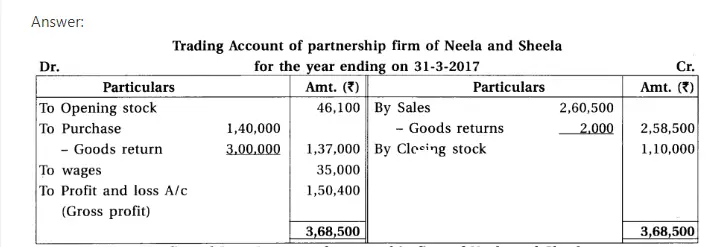
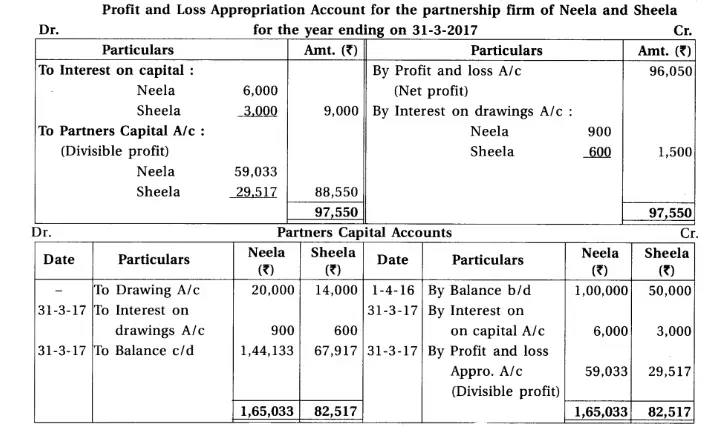
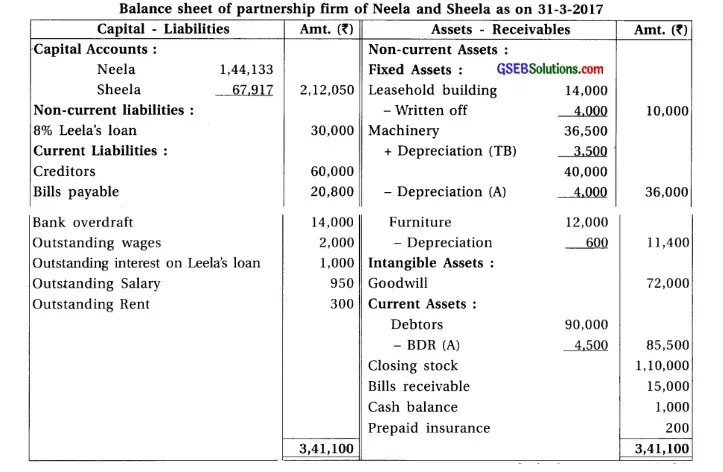
16. Neela and Sheela are partners of partnership firm sharing profit-loss in capital proportion.From the following trial balance and adjustments prepare final accounts of the firm.
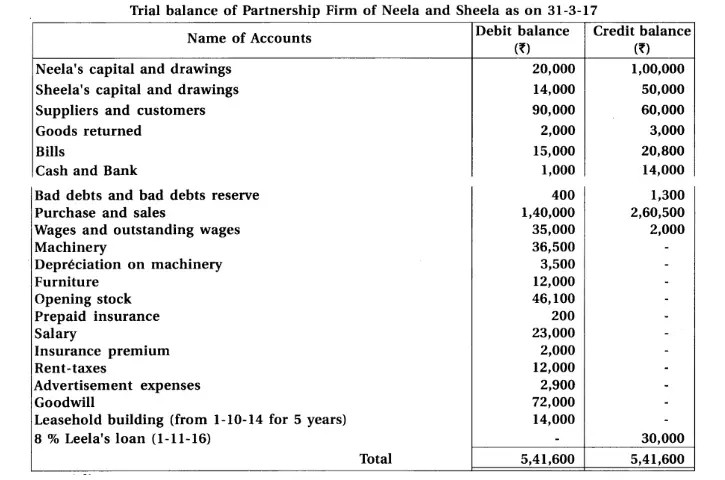
Adjustments :
(1) Closing stock ₹ 1,10,000 and having market value 20% more than book value. (2) Per annum 6% interest is payable on Partners’ capital. (3) Interest on drawings recoverable from partners : Neela ₹ 900, Sheela ₹ 600. (4) Provide 5% bad debt reserve on debtors. (5) Outstanding expenses at the end of accounting year : rent ₹ 300 and salary ₹ 950. (6) Provide depreciation : 10% on machinery and 5% on furniture.


Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
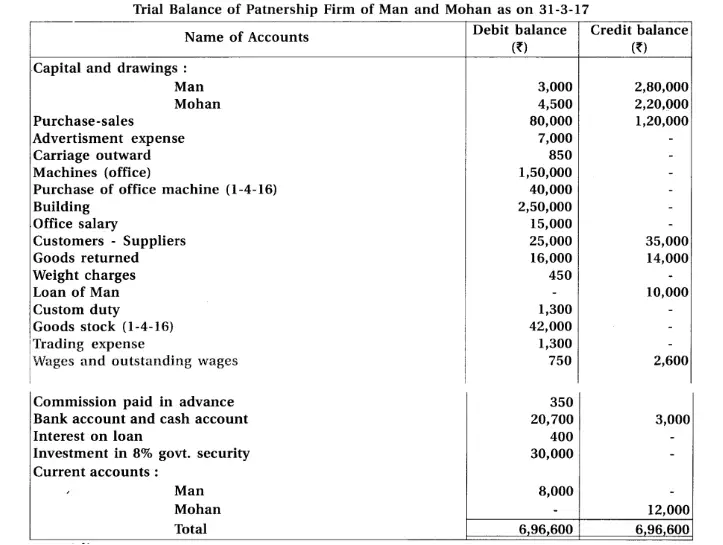
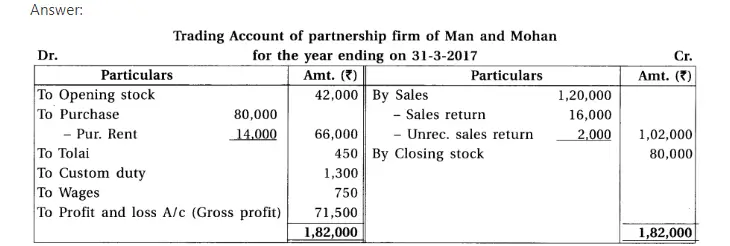
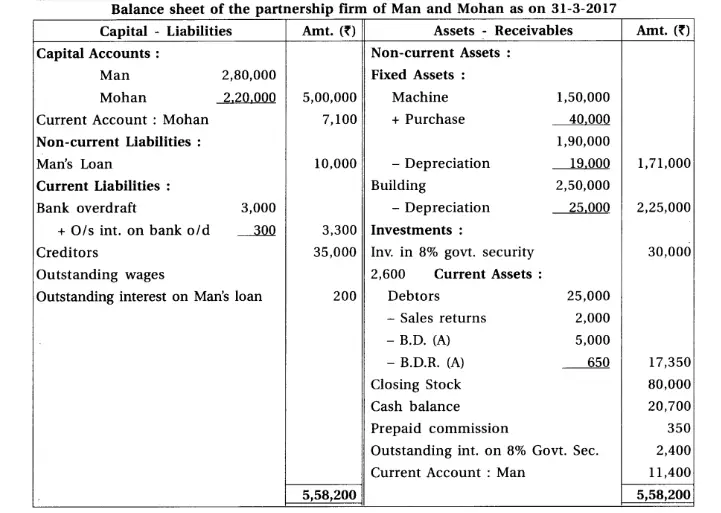
17. Man and Mohan are partners of a firm sharing profit and loss in the proportion of 1 : 1. From the given below trial balance and adjustments prepare final accounts for the year ending on 31-1-2017.
Adjustments :
(1) The value of closing stock is ₹ 80,000. It’s market value is 10% more. (2) Provide depreciation at 10% on machines and building. (3) Debtor of ₹ 10,000 became insolvent. 50% amount will be received as per instructions of his receiver. Provide 5% bad debt reserve. (4) 10% interest is outstanding on bank overdraft. (5) Goods of ₹ 2,000 is missed out to record in sales return book.



Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
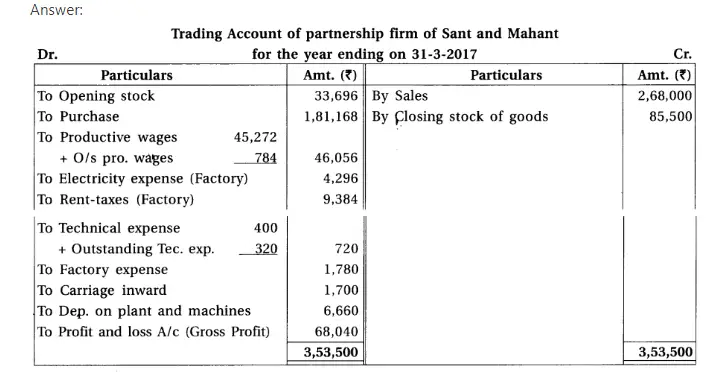
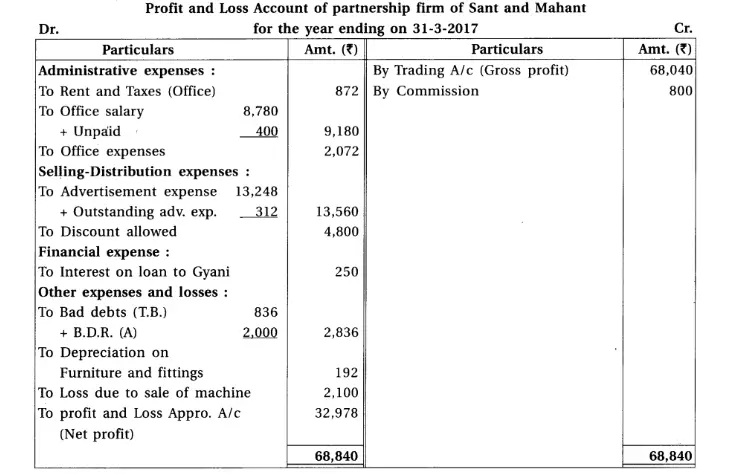
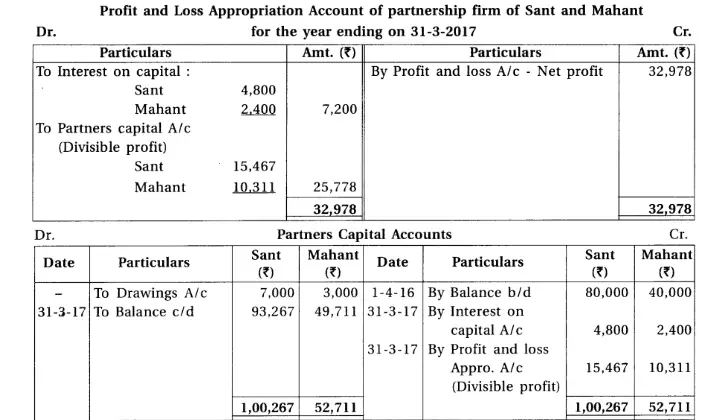
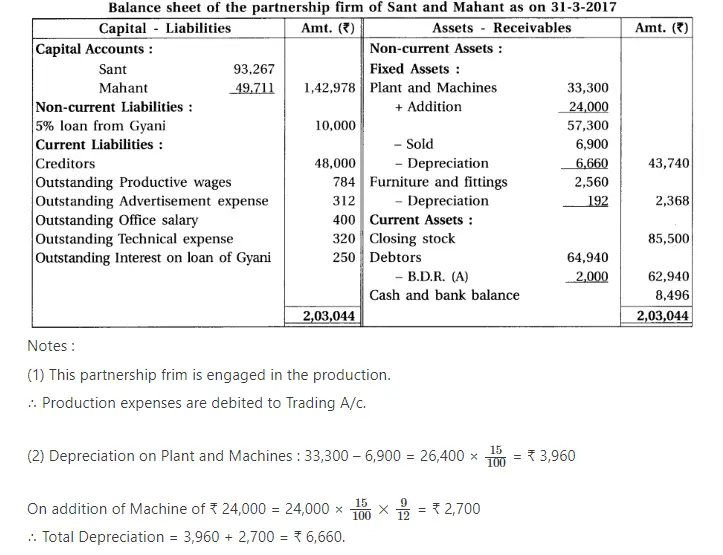
18. Sant and Mahant are partners of a firm sharing profit and loss in the proportion of 3 : 2. From the trial balance of 31-3-2017 and adjustments prepare final accounts of the partnership firm.
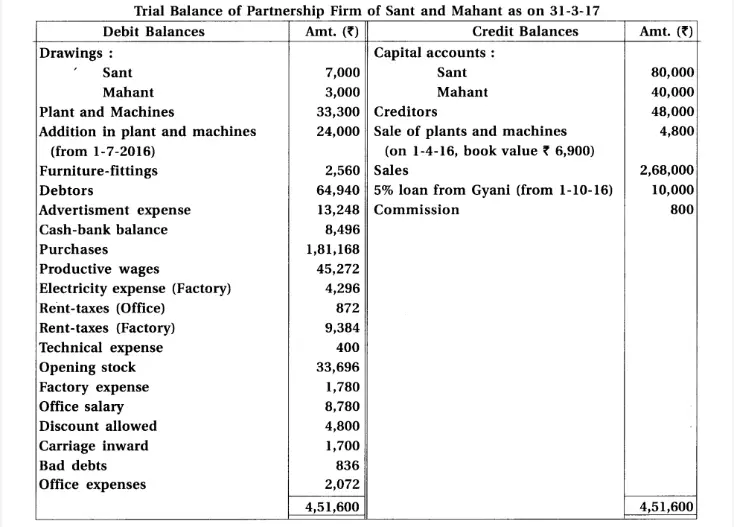
Adjustments :
(1) There was stock of ₹ 85,500. (2) Provide 15% depreciation on plant and machines and 7.5% on furniture and fittings. (3) Provide bad debts reserve of ₹ 2,000 on debtors. (4) 6% interest is payable on capital of partners. (5) Outstanding expenses : Productive wages ₹ 784, advertisement expense ₹ 312, office salary ₹ 400, technical expense ₹ 320.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
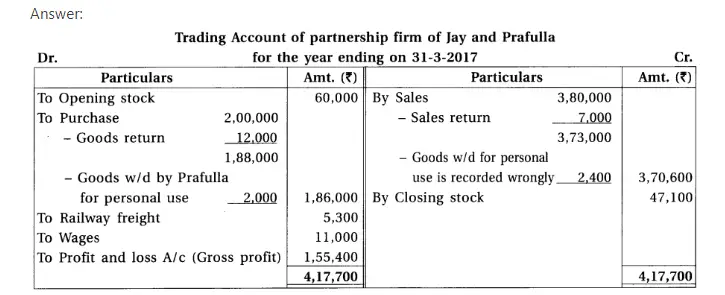
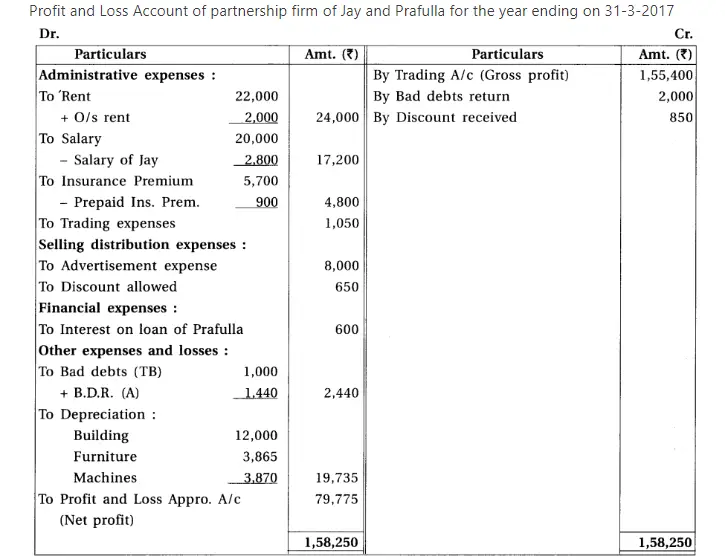
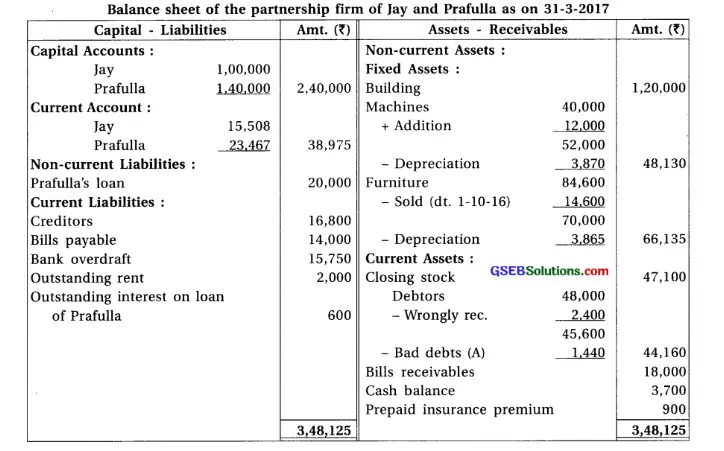
19. Jay and Prafulla are partners of a partnership firm sharing profit and loss in equal proportion. From the trial balance dated 31-3-17 and additional information, prepare financial accounts of the firm.
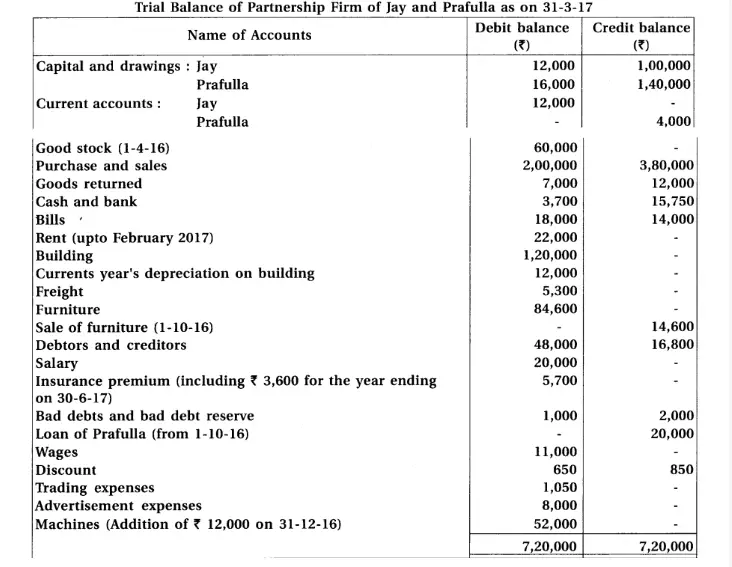
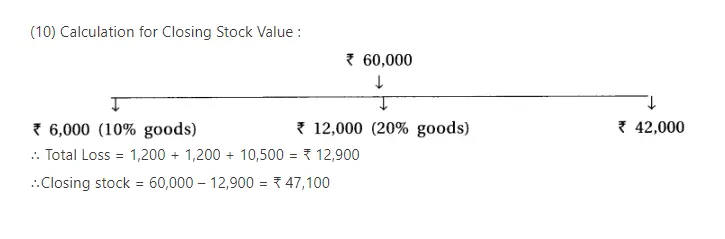
Adjustments : (1) The value of closing stock is ₹ 60,000. Out of which the market value of 10% goods is 20% less and the market value of 20% goods is 10% less. The remaining goods of ₹ 42,000 is valued at 25% less then book value. (2) Provide 10% interest on capital, 9% on balance of current accounts and 12% on drawings. (3) Monthly salary of ₹ 700 is payable to Jay. He has withdrawn salary of 4 months which is included in salary. (4) Prafulla has introduced additional capital of ₹ 20,000 on 1-1-17. (5) Jay has withdrawn ₹ 1,000 per month on the last date of each month. Prafulla has withdrawn on 1-10-2016. (6) Calculate depreciation at 9% on machines and 5% on furniture. (7) Prafulla has withdrawn goods of ₹ 2,000 on 1-12-2016, which is recorded in the sales book at ₹ 2,400. (8) One debtor of ₹ 2,400 became insolvent and 40 paise per rupee dividend is receivable.






Popular Videos

UX for Teams
Learn the basics and a bit beyond to improve your backend dev skills.

Designer

SEO & Instagram
Learn the basics and a bit beyond to improve your backend dev skills.

Designer
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
7. Write adjustment entries for the following adjustments :
(1) Book value of stock is ₹ 40,000, but its market value is 20% less than the book value. (2) Salary outstanding ₹ 1,000. (3) Mahendra landed loan of ₹ 25,000 to the firm, but 10% for 6 months is outstanding on it. (4) Interest received in advance ₹ 500. (5) Provide depreciation at 8% for 8 months on a building of ₹ 5,00,000. (6) Closing stock of stationery at the end of the accounting period is ₹ 250. (7) Closing balance at the end of accounting period, of debtors of business is ₹ 50,000, out which written off ₹ 4,500 as bad debts. Provide 10% bad debts reserve on debtors. (8) One partner has withdrawn goods of ₹ 5,000 for personal use, this transaction is not recorded. (9) Goods of ₹ 3,000 destroyed by fire. Insurance company has admitted the claim of 80%.

