Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Accoutancy
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
1. Select the correct answer for each questions :
1. What is the interest on partners’ capital for a partner ?
(A) An expense
(B) Liability
(C) Income
(D) Loss
2. Under which method, the interest on capital keeps on changing during the year due to the changes in the capital ?
(A) Fluctuating capital accounts method
(B) Fixed capital accounts method
(C) Current accounts method
(D) None of above
3. In which account and on which side the share of partners’ share profit is recorded under the fluctuating capital account method ?
(A) Debit to capital account
(B) Credit to capital account
(C) Debit to current account
(D) Credit to current account
4. At the end of the year where will you transfer drawings accounts in fixed capital account method ?
(A) To capital account
(B) To current account
(C) To profit and loss account
(D) To profit and loss appropriation account
5.How would you consider the interest on debit balance of pratners’ current account for firm ?
(A) An expense
(B) Liability
(C) Income
(D) Loss
6.What is the interest on drawings of partners for a partner ?
(A) An expense
(B) Liability
(C) Income
(D) Loss
7.Debit balance of profit and loss appropriation account means ………………
(A) Gross profit
(B) Gross loss
(C) Divisible profit
(D) Divisible loss
8. What percentage of interest will be paid, when no provision is made pertaining to interest on capital in the partnership deed ?
(A) 6%
(B) 9%
(C) 12%
(D) No interest
9. What percentage of interest will be paid on the loan lent by the partner to the firm, when no such provision is made in the partnership deed ?
(A) 6%
(B) 9%
(C) 12%
(D) No interest
10. The capital proportion of A, B and C is 3 : 2 : 1 respectively. The divisible profit is ₹ 66,000. What will be the amount of profit of C ?
(A) ₹ 11,000
(B) ₹ 22,000
(C) ₹ 33,000
(D) ₹ 66,000
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
2. Answer the following questions in one sentence :
1. What is partnership ?
Answer:
Partnership is the relation between the persons who have agreed to share the profit of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.
2. What is maximum and minimum limit of partners to constitute a partnership firm ?
Answer:
In the banking business minimum 2 and maximum 10 partners, while in the general firm
minimum 2 and maximum 20 partners are allowed.
As per Section-464 of Companies Act 2013, empowers the government to prescribe maximum number of partners to 100.
3. What is a partnership deed for a firm ?
Answer:
The partnership deed is a administrative constitution of partnership firm, where all provisions pertaining to firms administration are included.
4.Describe the objectives to prepare a partnership deed.
Answer:
Based on the written partnership deed, the solution of any misunderstanding or dispute in future can be obtained. On the basis of the provisions of the partnership deed.
5.How are the administrative problems solved, when no written agreement is signed between the partners ?
Answer:
In absence of written agreement / partnership deed, administrative problems can be solved with the help of provisions of Partnership Act 1932.
6. Describe state partners capital account methods of a partnership firm.
Answer:
There are two methods for partners capital account of a partnership firm.
(i) Fluctuating Capital Account method
(ii) Fixed Capital Account method.
7. Profit of a partner is credited to which account under fixed capital account method ?
Answer:
Profit of a partner is credited to current account under fixed capital account method.
8. Additional capital introduced by partner on permanent basis is credited to which account in the fixed capital account method ?
Answer:
Additional capital introduced by partner on permanent basis is credited to fixed capital account itself.
9. The debit balance of current account of partners is shown on which side of balance sheet ?
Answer:
The debit balance of current account of partners is shown on Assets – Receivables side of balance sheet.
10. Write a journal entry to transfer drawings account to the capital account, at the end of the year.
Answer:
Partners’ capital A/c Dr.
To Partners’ drawings A/c
(Being transfer drawings account amount to capital account at the end of the year)
11. Profit and loss appropriation account is a part of which account ?
Answer:
Profit and loss appropriation account is a part of profit and loss account.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
3. Answer the following questions in brief :
1.A partner withdraws identical amount at the end of each month from the firm. At the end of the year total annual drawings is ₹ 12,000. 12 % p.a. interest is chargeable on drawings. Determine the amount of interest on drawings of the year.

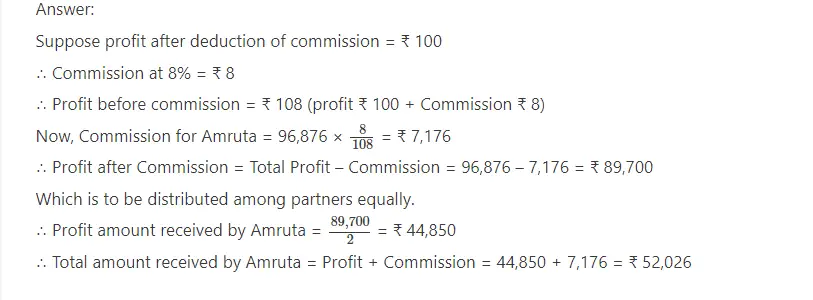
2. Amruta and Divya are the partners of a firm. Their capital ratio is 3 : 2. Amruta is to be paid 8% commission on net profit, after deduction of such commission. What amount will be received by Amruta if profit of the year is ₹ 96,876.
3.Vismay, Abhjit and Kunal are partners sharing profit-loss in the proportion of 3 : 2 : 4.
Manger is to be paid 10% commission on profit but after the deduction of his such share the share of profit of Abhijit is ₹ 30,000. Determine the commission of manager.
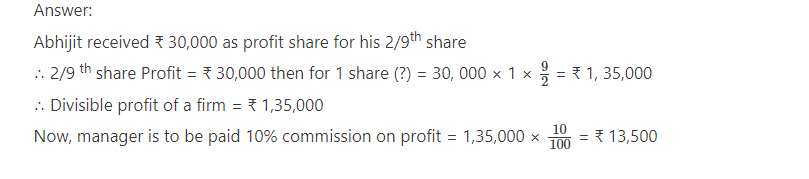
4. The profit-loss sharing ratio of Rajkumar, Kaushik and Sharma is 15 : 10 : 9. The total profit of the year of the firm is ₹ 68,000. Determine the share in profit of each partner.

5.Mehta receives his share four times of Pandya. While Bajpai receives half of share of Mehta. Profit of firm at the end of the year is ? 87,500. Determine the share in profit of each partner.

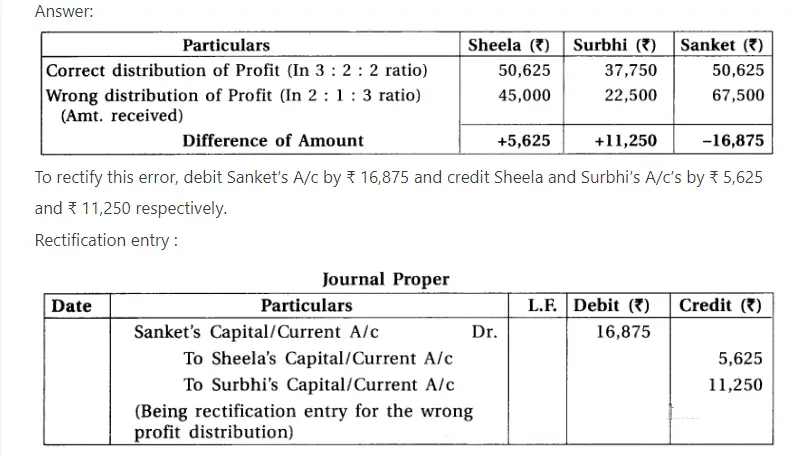
6.Profit of the partnership firm of Sheela, Surbhai and Sanket is ₹ 1,35,000. They have shared profit in the ratio 2:1:3 instead of 3 : 2 : 3. What accounting treatment is to be given to the capital account to rectify this error ?
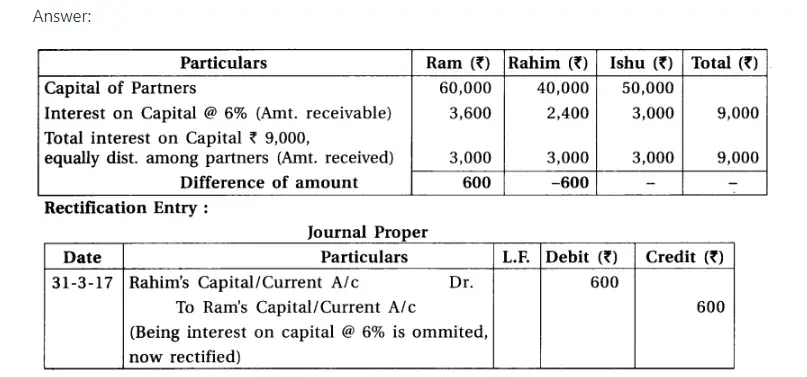
7.Ram, Rahim and Ishu are partners of a partnership firm. Their capital as on 1-4-2016 was ₹ 60,000, ₹ 40,000 and ₹ 50,000 respectively. After the distribution of the profit of the year, it was realized that charging of 6% interest on partners’ capital accounts was missed out. Write an entry for the rectification of error.
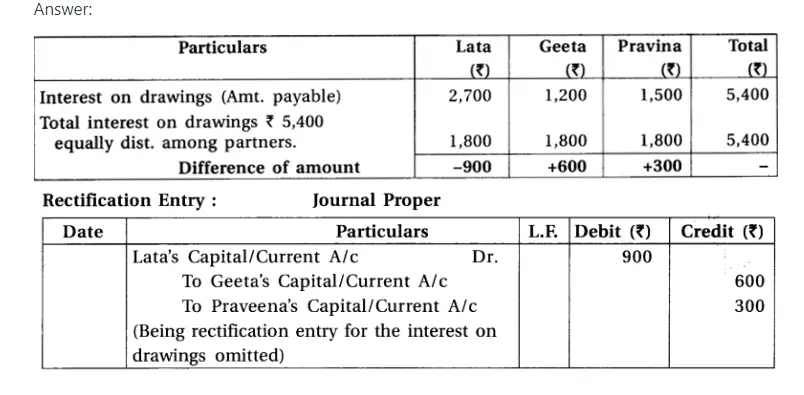
8.Lata, Geeta and Pravina are partners of a partnership firm. After distribution of the profit of the year it was realized that charging of interest on partners’ drawings account respectively ₹ 2,700, ₹ 1,200 and ₹ 1,500 was missed out. Write an entry for the rectification of error.
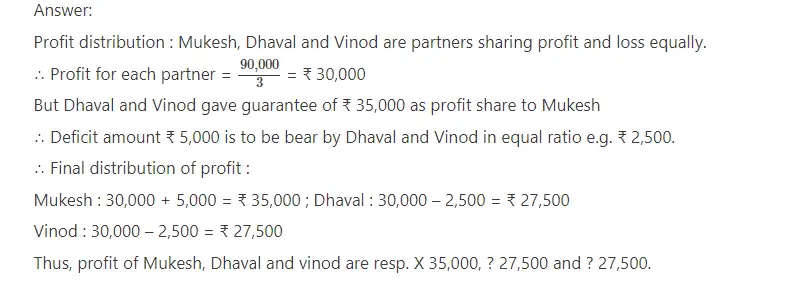
9.Mukesh, Dhaval and Vinod are the partners of a partnership firm. Their capital proportion is 4 : 2 : 3. Dhaval and Vinod has given assurance to Mukesh that he will get minimum ₹ 35,000 form the profit. The profit of the year is ₹ 90,000. How would you distribute the profit among the partners ?
10.The closing capital of Raghuvir is ₹ 80,000. In which ₹ 12,5000 drawings of current year and profit of ₹ 17,800 are recorded. What will be the interest at 6% p.a. on the opening capital ?

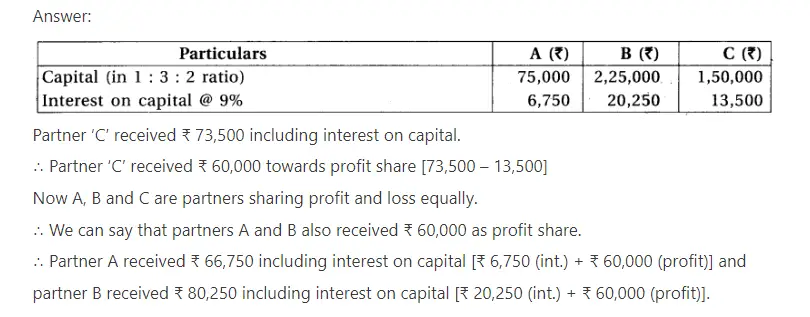
11. A, B and C are the partners sharing profit- loss in equal proportion. Their total capital is of ₹ 4,50,000. Their proportion of capital is 1 : 3 : 2. Firm pays interest on capital at 9% p.a. Partner C has received ₹ 73,500 including interest on capital. Determine the amount payable including interest on the capital of A and B ?
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
4. Answer the following questions to the point :
1. Explain the meaning of partnership.
Answer:
As per Indian Partnership Act 1932, Section-4, ‘Partnership is the relation between the persons who have agreed to share the profit of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.’
As per Luise Henny, ‘two or more persons who are competent to undertake a contract to earn profit from a legal business is termed as partnership.
Thus, (1) partnership is created by contract. (2) Person who are competent to undertake a contract to earn profit from a legal business is known as partnership. (3) The person who enter into such relationship are individually called ’Partners’. (4) The business run collectively in partnership by two or more persons is known as partnership firm.
2. Describe the Characteristics of partnership.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of partnership :
(1) Creation by Contract: Partnership emerges through agreement. Partnership agreement can be in written or oral form. But written form of partnership deed is desirable and advisable.
(2) Profit Objective : Partnership firm takes place to earn and distribute profit. Distribution of profit or loss is done among partners in their predetermined proportion. If nothings is mentioned regarding profit-loss ratio, profit or loss is distributed among partners in equal ratio.
(3) Legal Business : Partnership firm is formed to do a legal business.
(4) Agent of each other : The business of partnership firm is run by all the partners or any one of them for all or more than one partner. Thus, we can say that each partner is an agent of each other.
(5) Number of partners : In the banking business minimum two and maximum ten while in general business firm minimum two and maximum twenty partners are allowed. Now a days, government restricted maximum number of partners in a firm to be 50 vide rule-10 of companies (Miscellaneous) Rules 2014.
(6) Unlimited Liabilities : As per Partnership Act, partners are responsible to pay business obligation from their personal property when the firm does not have sufficient assets to pay liabilities of the business. Every partner individually and collectively responsible to the partnership firm. Therefore, the liability of each partner is unlimited.
(7) Ownership and management : Partners are owners of the business and they do the management of the business. The management of business is done either by all the partners or by one partner or by more than one partner.
(8) Legal status : In Indian Partnership Act 1932, partners rights, duties, laws, registration of the firm and other provisions related to partnership are shown.
3. Describe the accounting provisions of partnership Act 1932, in absence of a partnership deed.
Answer:
The following provisions of partnership Act 1932, will be applicable if no partnership deed is prepared or no clarification is made in the partnership deed.
Each partner contributes capital in the firm by mutual agreement. It is not mandatory to bring a capital for each partner.
Interest on capital cannot be paid and interest on drawings cannot be charged.
The distribution of profit and loss would remain in equal ratio.
Salary, bonus, commission or remuneration cannot be paid to the partners.
6% p.a. interest is payable for the loan given by any partner to the firm.
In case of any reasonable expense incurred by the partner for the firm, the partner has right to reimburse it.
4. What is profit-loss appropriation account ? Which items are disclosed in it ?
Answer:
Profit-loss appropriation account –
1. Profit-loss appropriation account is a special account to show the distribution of profit or loss among the partners of a firm.
2. Profit and loss appropriation account is always prepared after preparing profit and loss account.
3. Net profit or Net loss is carried forward to this account from profit and loss account.
4. By preparing profit and loss appropriation account, net divisible profit or loss can be known.
5. It is not compulsory to prepare profit and loss appropriation account separately.
6. Particulars included in the profit and loss appropriation account are shown below (In specimen form)
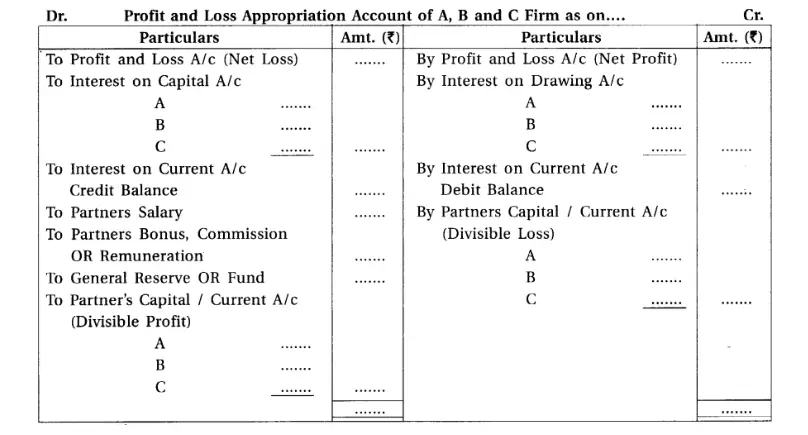
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
4. Answer the following questions to the point :
1. Explain the meaning of partnership.
Answer:
As per Indian Partnership Act 1932, Section-4, ‘Partnership is the relation between the persons who have agreed to share the profit of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.’
As per Luise Henny, ‘two or more persons who are competent to undertake a contract to earn profit from a legal business is termed as partnership.
Thus, (1) partnership is created by contract. (2) Person who are competent to undertake a contract to earn profit from a legal business is known as partnership. (3) The person who enter into such relationship are individually called ’Partners’. (4) The business run collectively in partnership by two or more persons is known as partnership firm.
2. Describe the Characteristics of partnership.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of partnership :
(1) Creation by Contract: Partnership emerges through agreement. Partnership agreement can be in written or oral form. But written form of partnership deed is desirable and advisable.
(2) Profit Objective : Partnership firm takes place to earn and distribute profit. Distribution of profit or loss is done among partners in their predetermined proportion. If nothings is mentioned regarding profit-loss ratio, profit or loss is distributed among partners in equal ratio.
(3) Legal Business : Partnership firm is formed to do a legal business.
(4) Agent of each other : The business of partnership firm is run by all the partners or any one of them for all or more than one partner. Thus, we can say that each partner is an agent of each other.
(5) Number of partners : In the banking business minimum two and maximum ten while in general business firm minimum two and maximum twenty partners are allowed. Now a days, government restricted maximum number of partners in a firm to be 50 vide rule-10 of companies (Miscellaneous) Rules 2014.
(6) Unlimited Liabilities : As per Partnership Act, partners are responsible to pay business obligation from their personal property when the firm does not have sufficient assets to pay liabilities of the business. Every partner individually and collectively responsible to the partnership firm. Therefore, the liability of each partner is unlimited.
(7) Ownership and management : Partners are owners of the business and they do the management of the business. The management of business is done either by all the partners or by one partner or by more than one partner.
(8) Legal status : In Indian Partnership Act 1932, partners rights, duties, laws, registration of the firm and other provisions related to partnership are shown.
3. Describe the accounting provisions of partnership Act 1932, in absence of a partnership deed.
Answer:
The following provisions of partnership Act 1932, will be applicable if no partnership deed is prepared or no clarification is made in the partnership deed.
Each partner contributes capital in the firm by mutual agreement. It is not mandatory to bring a capital for each partner.
Interest on capital cannot be paid and interest on drawings cannot be charged.
The distribution of profit and loss would remain in equal ratio.
Salary, bonus, commission or remuneration cannot be paid to the partners.
6% p.a. interest is payable for the loan given by any partner to the firm.
In case of any reasonable expense incurred by the partner for the firm, the partner has right to reimburse it.
4. What is profit-loss appropriation account ? Which items are disclosed in it ?
Answer:
Profit-loss appropriation account –
1. Profit-loss appropriation account is a special account to show the distribution of profit or loss among the partners of a firm.
2. Profit and loss appropriation account is always prepared after preparing profit and loss account.
3. Net profit or Net loss is carried forward to this account from profit and loss account.
4. By preparing profit and loss appropriation account, net divisible profit or loss can be known.
5. It is not compulsory to prepare profit and loss appropriation account separately.
6. Particulars included in the profit and loss appropriation account are shown below (In specimen form)

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
5. Write Short Notes on :
1. Partnership deed :
A partnership deed is essential for defining the terms of a partnership agreement and ensuring clarity and accountability among partners. It serves as the administrative constitution of the partnership firm, encompassing various provisions related to firm administration. Typically, a partnership deed includes:
1. Partner Details: Names, addresses, and other relevant information of partners.
2. Firm Details: Name, address, objectives, and nature of the business.
3. Commencement Date: The date of partnership establishment.
4. Capital Contributions: Amount of capital contributed by each partner, though not mandatory for every partner.
5. Interest on Capital: Whether interest is payable on capital contributions.
6. Drawings Limit: Maximum withdrawal limits for partners.
7. Interest on Drawings: Whether interest is charged on partner withdrawals.
8. Profit-Loss Distribution: Proportions for sharing profits or losses among partners.
9. Partner Compensation: Provisions for salary, bonus, commission, and remuneration.
10. Interest on Partner Loans: Terms for interest on loans given by partners to the firm.
11. Goodwill Valuation: Methods for valuing goodwill during partner admissions, retirements, or deaths.
12. Partner Changes: Procedures for partner admissions, retirements, or deaths.
13. Firm Dissolution: Conditions and procedures for firm dissolution.
A well-drafted partnership deed provides a legal framework for the partnership, facilitates dispute resolution, and protects the interests of all partners.
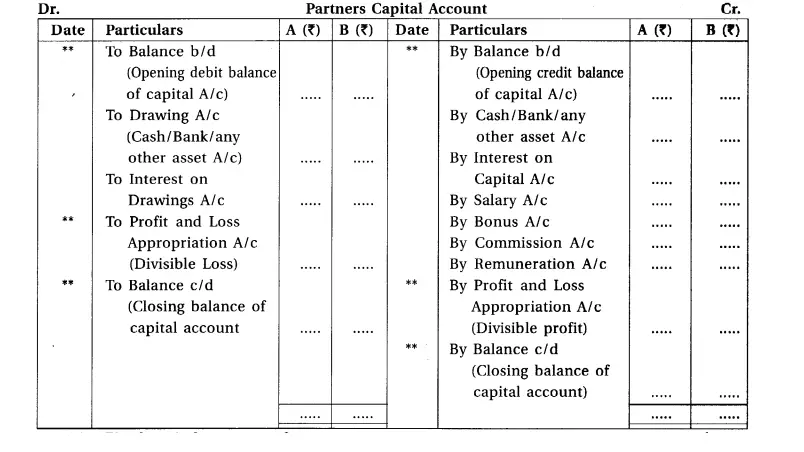
2. Fluctuating capital accounts of partners :
A method in which the opening balance of the capital account and the closing balance of the capital account of any partner is reported . fluctuated then it is known as Fluctuating or Temporary capital account method.
Under this method, to record all the transactions related to the partners, only one capital account is prepared in the books of the firm.
Under this method, balance of partners capital account has either debit or credit balance.
If there is credit balance in capital account, it would appear at the liability side of balance sheet and
If there is debit balance in capital account it would appear at the asset side of balance sheet.
The balances which are to be included in the partners capital account on the debit and
credit side, are as follows (specimen of account)
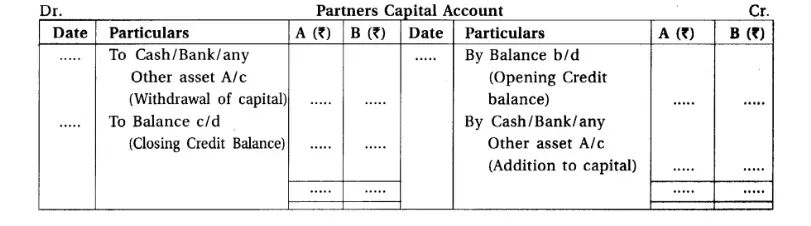
3.Fixed capital accounts of partners :
The Fixed Capital Account Method is a partner capital approach where the opening and closing balances in partners’ capital accounts remain unchanged. Here’s how it operates:
-Two Accounts Maintained:
– Partners’ Capital Account: Records long-term changes, such as additional capital injections or permanent withdrawals.
– Partners’ Current Account: Documents short-term changes, including interest on capital, drawings, salary, bonuses, commissions, and interest on loans.
– Capital Account Contents: The capital account captures permanent alterations, while the current account tracks temporary adjustments.
– Balance Sheet Presentation:
– The credit balance in the partners’ capital account is reflected on the capital and liabilities side of the balance sheet.
This method offers a structured approach to managing partner transactions, distinguishing between permanent capital changes and temporary adjustments.
4.Current accounts of partners :
In the Fixed Capital Account Method, the record of partner transactions with the partnership firm, excluding permanent capital changes, is kept in the current account.
– Balance Flexibility: The closing balance in a partner’s current account can be either a debit or credit balance.
– Balance Determination: If the total on the credit side exceeds the total on the debit side, the current account holds a credit balance.
– Balance Sheet Presentation:
– A debit balance in the current account appears on the capital liability side of the balance sheet.
– A credit balance in the current account is shown on the asset receivable side of the balance sheet.
This method facilitates tracking of partner transactions beyond permanent capital adjustments while providing clarity on the financial position of each partner.

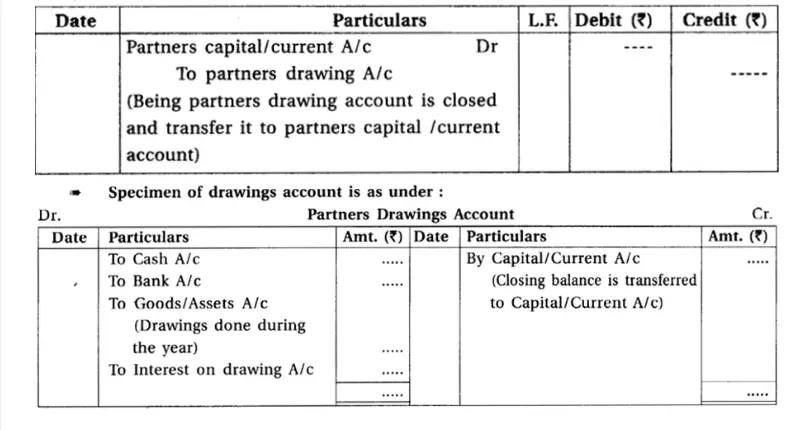
5.Drawings accounts of partners :
Drawings accounts of partners are created when a partner withdraws cash, goods, or assets from the partnership for personal use.
– Nature of Drawings: Withdrawn amounts by partners for personal use are termed as “drawings.”
– Interest on Drawings: If specified in the partnership deed, interest on drawings is also debited to the partner’s drawings account.
– Year-End Procedure:
– For the Fluctuating Capital Account Method: At the end of the accounting period, the drawing account is closed, and the balance is transferred to the partner’s capital account.
– For the Fixed Capital Method: In this method, the balance in the drawing account is debited to the partner’s current account at the end of the accounting year.
This approach ensures accurate recording of partner withdrawals and facilitates appropriate adjustments at the year-end according to the chosen capital accounting method.
Jornal entry for the same is
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
6. Distinguish between :
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Fixed Capital Account Method
Meaning :-
1. Where the opening balance and the closing balance of the partners capital account is reported unchanged is known as fixed capital account method.
2. Accounts :-
To record all the transactions of the partners with the firm two accounts are opened in the books of the firm. (i) Capital account and (ii) Current account
Fluctuating Capital Account Method
Meaning :-
1. Where the opening balance and the closing balance of the partners capital account is reported flexible is known as fluctuating capital account method.
2. Accounts :-
To record all the transactions of the partners with the firm only capital account is opened in the books of the firm.
3. Treatment of Transaction :-
In ‘capital account’, capital and changes in capital are recorded. Transaction as other than permanent capital are recorded in the current account.
4. Balance of Account
Fixed capital account has always credit balance and current account can have a debit or credit balance
3. Treatment of Transaction :-
All transactions of capital and other than capital are recorded in the ‘capital account’…………………………………………..
4. Balance of Account :-
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Q.7 X and Y are partners of a partnership firm. They have not prepared partnership deed. There is difference of opinion between the partners. Please give legal advice to the partners.
(1) X demands 6% p.a. interest on drawings of partners. (2) Y is an active partner of the firm. He claims for remuneration and commission. (3) X demands interest on capital of partners. (4) X has lent loan of ₹ 20,000 to the firm. He demands interest on loan. (5) Firm has lent loan of ₹ 25,000 to Y. X demands to charge interest on the laon. (6) X demands to share profit between the partners in the proportion of capital.
Answer:
When partnership deed is not prepared or provision is not there in the partnership deed, then as per provision of partnership Act 1932 –
(1) Interest on drawings cannot be charged. (2) No remuneration or commission will be paid to partner Y. (3) Interest on capital cannot be paid/given to the partners. (4) Interest on loan to the firm given by partner X ₹ 1,200 is to be paid. i.e. @ 6% p.a. on ₹ 20,000. (5) Interest on loan given by firm to partner Y cannot be recovered. (6) Profit will be distributed equally among partners of the firm, and not in the capital ratio.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
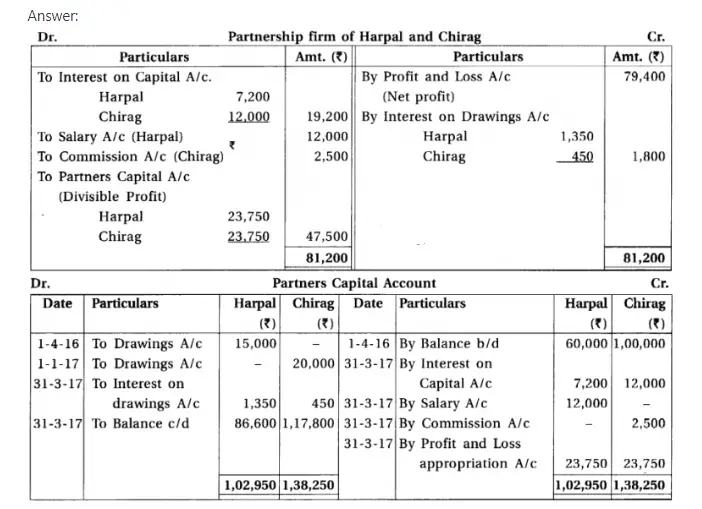
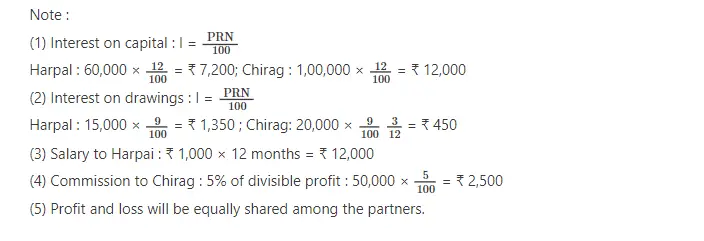
Q.8 Harpal and Chirag are the partners of a firm. On 1-4-2016 their capital is ₹ 60,000 and ₹ 1,00,000 respectively. During the year on 1-4-2016 Harpal has withdrawn ₹ 15,000 and Chirag has withdrawn ₹ 20,000 on 1-1-2017. Provisions of partnership deed are as follows:.
(1) Provide 12% p.a. interest on capital. (2) Charge 9% p.a. interest on drawings. (3) ₹ 1,000 per month are payable to Harpal for his active role in the firm, while 5% commission of divisible profit is payable to Chirag.
On 1-12-2016 Harpai has given loan of 30,000 to the firm. There is no provision for Interest on loan in the partnership deed. He claims 11% interest on his loan. The profit to the firm on 31-3-2017 was 79,400, before above mentioned provisions but after charging interest on loan of Harpal.
From the above information, prepare profit and loss appropriation account and partners capital accounts.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Q.9
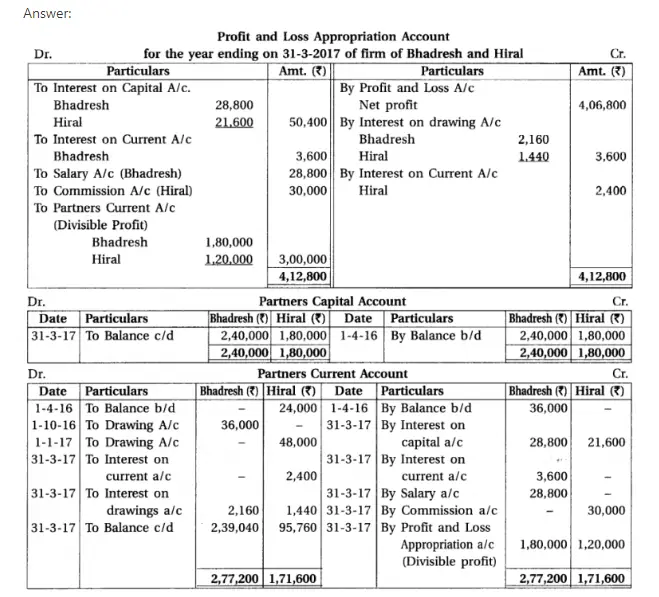
Q.9 Bhadresh and Hiral are the partners of a firm. Their profit- loss sharing ratio is 3 : 2. On 1-4-2016 total capital of partners was. ₹ 4,20,000. The proportion of their fixed capital is 4 : 3. On this day, balances of their current accounts are as follows: Bhadresh ₹ 36,000 (credit), Hiral 24,000 (debit). As per partnership deed per annum 12% interest is payable on the capital of the partners. Provide per annun 10% interest on opening balances of the current accounts. Per annum 12% interest is to be charged on drawings. ₹ 2,400 per month as a salary are payable to Bhadresh for his active role in the firm.
On 1-10-2016 Bhadresh has withdrawn ₹ 36,000 and on 1-1-2017 Hiral has withdrawn ₹ 48,000. 10% commission on net profit is payable Hiral, from net profit, but after deduction of his such share from net profit.
Before consideration of above mentioned adjustmets the profit for the year ending on 31-3-2017 of the firm was ₹ 4,06,800.
From the above information prepare profit and loss appropriation account and partners capital account and current accounts as per the fixed method.

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Q.10
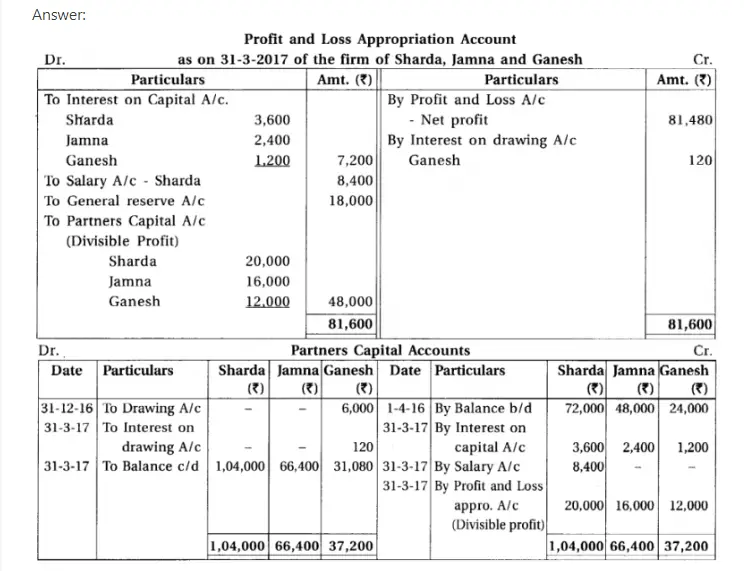
Q.10 Sharda, Jamna and Ganesh are the partners of a firm. On 1-4-2016 their capital was ₹ 72,000; ₹ 48,000 and ₹ 24,000 respectively.
As per the partnership deed : (1) 5% per annum interest is payable on opening capital of partenrs. (2) 8% per annum interest will be charged on drawings. (3) Monthly salary of ₹ 700 is payable to Sharda. (4) Half profit will be distributed amongst the partners in equal proportion and remaining half profit in the proportion oftheir opening capital.
On 31-12-2016 Ganesh has withdrawn ₹ 6,000 from the firm for his personal use. Profit of the firm for the year ending on 31-3-2017 after charging interest on drawings but before consideration of above mentioned adjustment was ₹ 81,600. Before the distribution of the profit to the partners but after consideration of above mentioned adjustments from surplus of profit 20% (but not less than ₹ 18,000) are to be transferred to the general reserve.
From the above information for the year ending on 31-3-2017, prepare profit-loss appropriation account and partners’ capital accounts.

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Q.11
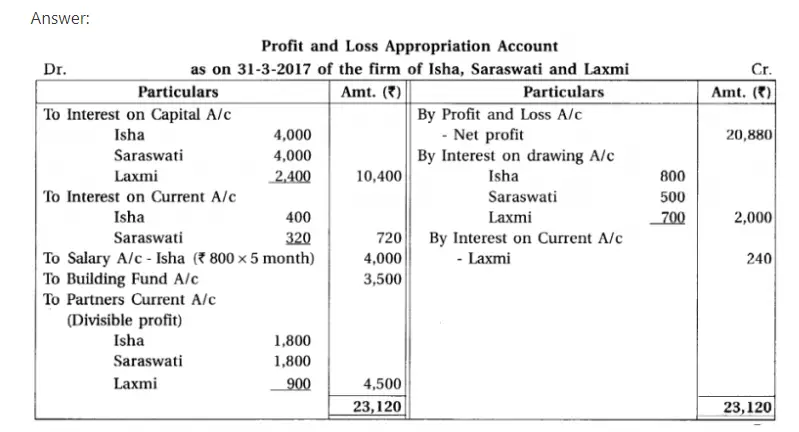
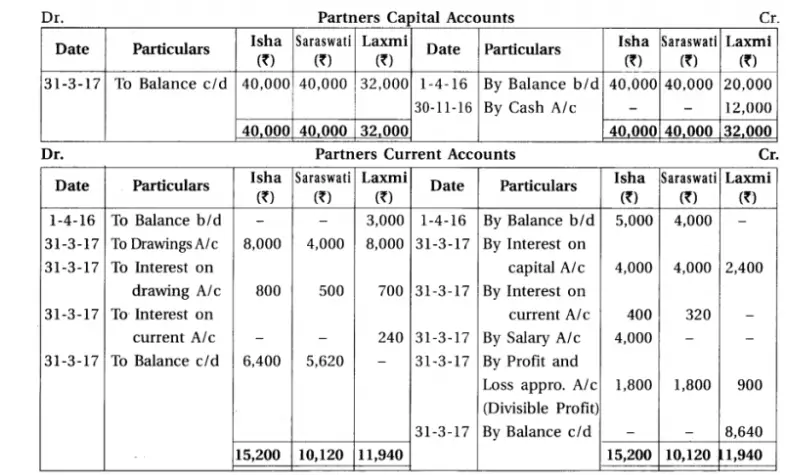
Q.11 Isha, Saraswati and Laxmi are the partners sharing profit-loss in the proportion of opening capital. On 1-4-2016 balance of their fixed capital accounts were ₹ 40,000; ₹ 40,000 and ₹ 20,000 respectively. On the same day balance of their current accounts were as under :
Isha ₹ 5,000 (credit), Saraswati ₹ 4,000 (credit) and Laxmi ₹ 3,000 (debit).
Total drawings of partners during the year is ₹ 20,000. It is in the proportion of 2 : 1 : 2. On 30-6-2016 Isha has lent ₹ 3,000 and on 1-10-2016 ₹ 2,000 to the firm in the form of loan. On 30-11-2016 Laxmi has introduced addition capital of ₹ 12,000.
As per the partnership deed : (1) Provide 10% p.a. interest on capital. (2) Respectively ₹ 800, ₹ 500 and ₹ 700 are to be recovered as interest on drawings. (3) Provide 8% p.a. interest on opening capital of current accounts. (4) From 1-11-2016 monthly salary of ₹ 800 is payable to Isha for her active role in the firm. (5) ₹ 3,500 of divisible profit are to be transferred to building fund account.
Profit for the year ending on 31-3-2017 before incorporation of above mentioned adjustment but after incorporation of effect of interest on Isha’s loan was ₹ 20,880.
Prepare profit and loss appropiration account, capital accounts and current accounts of partners.

Chapter 1 Introduction to Partnership
Q.12
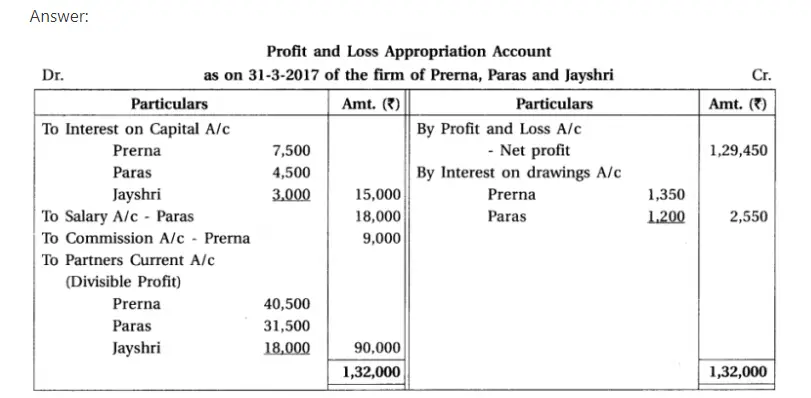
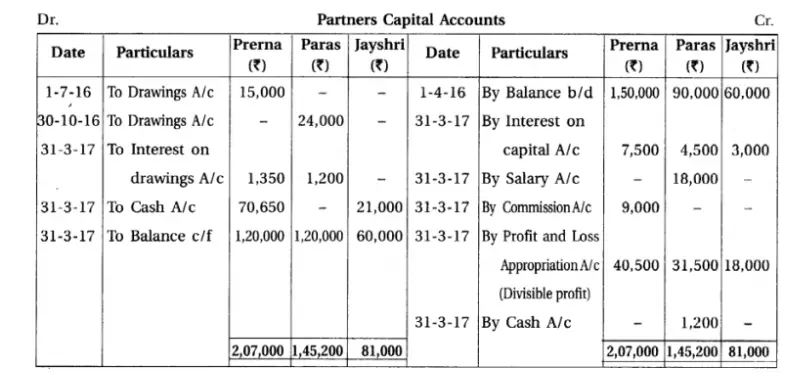
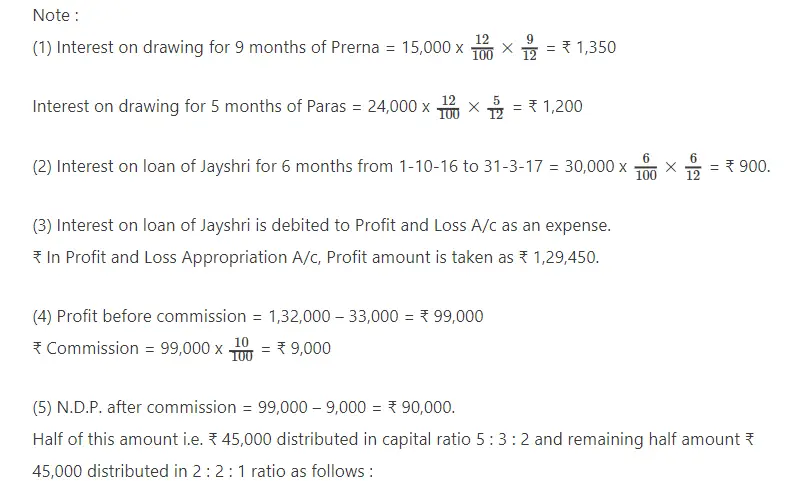
Q.12Prerna, Paras and Jaishri are the partenrs of a firm. On 1-4-2016 their capital was ₹ 1,50,000; ₹ 90,000 and ₹ 60,000 respectively. Their drawings were as follows :
Prerna ₹ 15,000 on 1-7-2016 and Paras ₹ 24,000 on 30-10-2016.
They distribute half profit in the capital proportion and remaining in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. Jaishri has lent out loan of ₹ 30,000 on 1-10-2016 to the firm. As per partnership deed per annum 5% interest on capital, per annum 12% interest on drawings is to be calculated. Paras is to be paid annual salary of ₹ 18,000 for his active role in the firm. 10% commission is to be given to Prerna from surplus of profit after providing for above mentioned provisions and after deduction of her such commission. For the year ending on 31-3-2017 profit of the firm before incorporation of the above mentioned adjustmetns but after charging interest on loan of Jaishri was ₹ 1,29,450.
It was decided that after the consideration of above mentioned adjustments and transfer of profit-loss to capital account, total capital of the firm would be identical to the opening capital, which should be in the proportion of 2:2 :1. For this purpose required amount will be introduced by the partners and excess amount will be withdrawn by the partners.
Prepare profit and loss appropriation account, partners’ capital accounts for the year ending on 31-3-2017.




Popular Videos

UX for Teams
Learn the basics and a bit beyond to improve your backend dev skills.

Designer

SEO & Instagram
Learn the basics and a bit beyond to improve your backend dev skills.

Designer